Sectieoverzicht
-
-
Surface tension is the tendency of fluid surfaces to shrink into the minimum surface area possible. Cohesive forces between molecules cause the surface of a liquid to contract to the smallest possible surface area. This general effect is called surface tension.
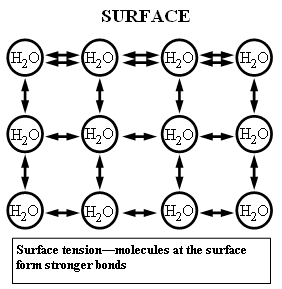
Figure 1: Water molecules attract one another, as each molecule forms a bond with the ones close to it. At the surface, though, the outmost layer of molecules, has fewer molecules to cling to, therefore compensates by establishing stronger bonds with its neighbors, this leading to the formation of the surface tension.
The surface tension of liquid decreases with an increase in temperature. As the temperature increases, the liquid molecules become more energetic and start moving in random directions, thereby decreasing the strength of the intermolecular bonds.
Examples of Surface Tension
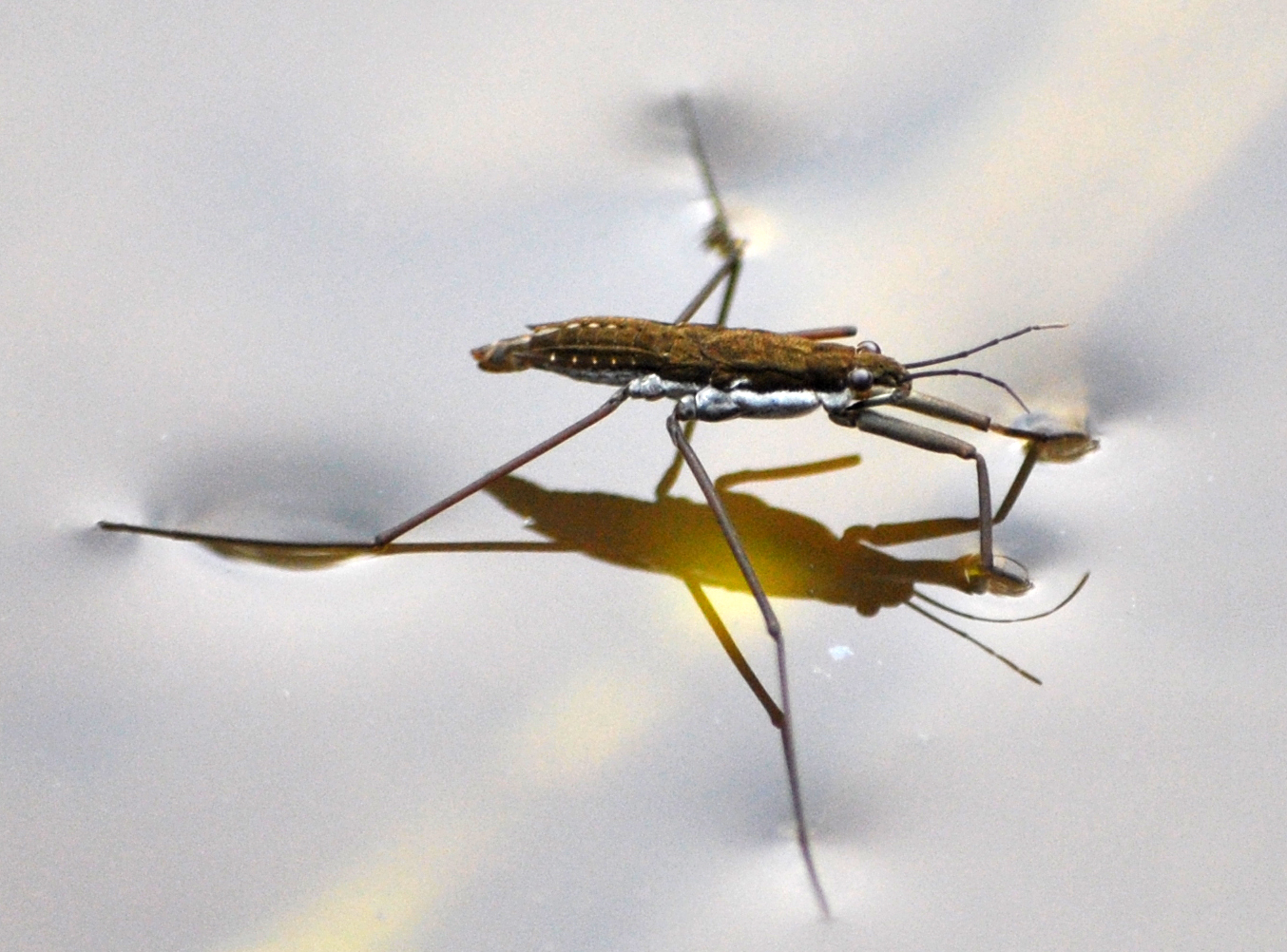

Figure 2: Water striders, which are small insects, can walk on water as their weight is less to penetrate the water surface.
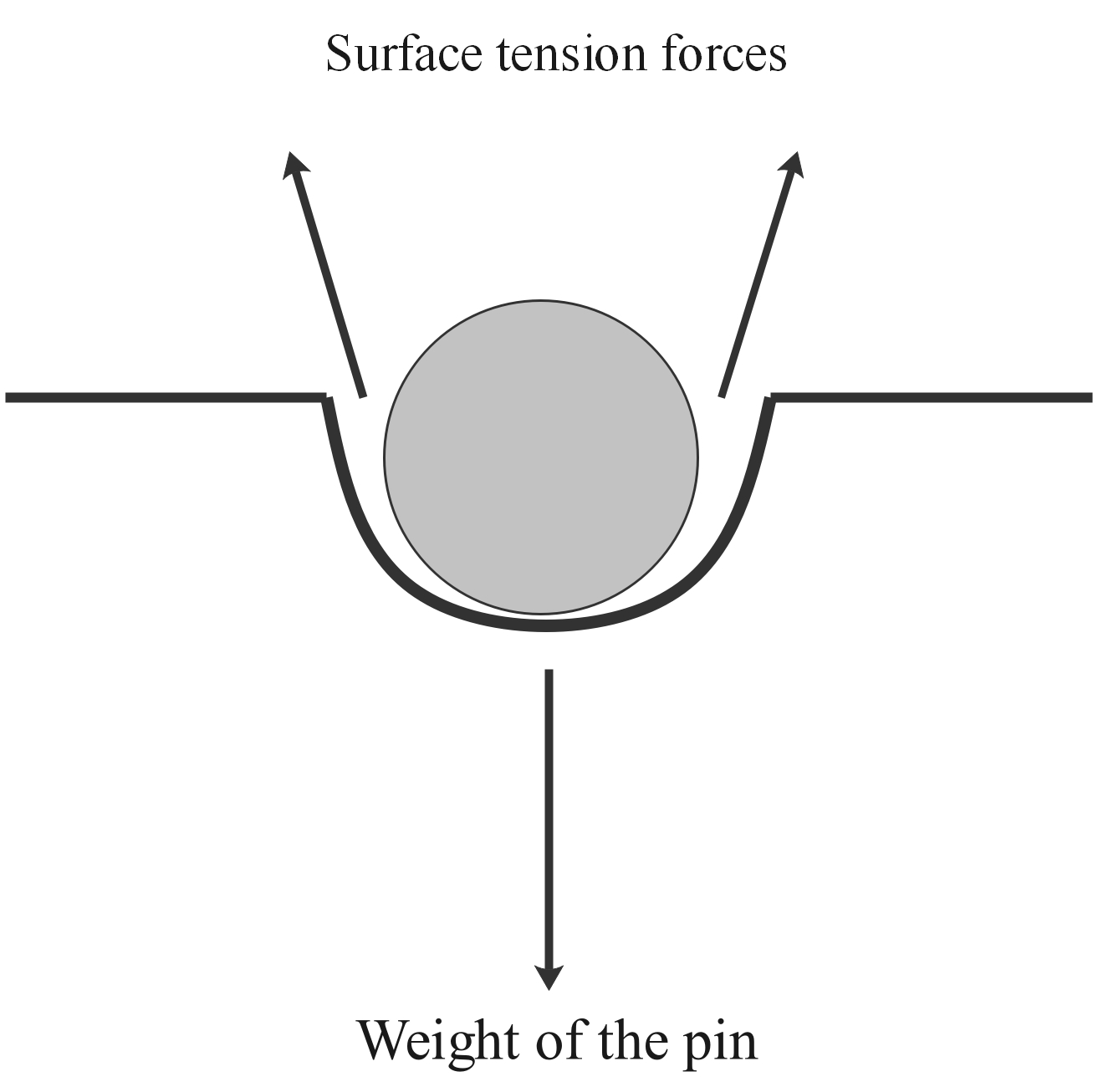
Figure 2: a pin or needle can float on the surface of water because the downward force of the needle's weight is balanced by the upward forces of surface tension from the liquid.
Like these, there are various examples of surface tension which are found in nature. Some cases are provided below:
- Rainproof tent materials where the surface tension of water will bridge the pores in the tent material
- Cleaning of clothes and dishes by soaps and detergents which lowers the surface tension of the water. This happens because the molecules of soap weaken the forces of attraction between water molecules, effectively reducing the surface tension of the water.
- Round bubbles where the surface tension of water provides the wall tension for the formation of water bubbles.

Figure 3: The round bubbles are formed by surface tension
This phenomenon is also responsible for the shape of liquid droplets.
Activity 1
What you will need:
A dish
Milk
Food coloring
Liquid dish soap
One earbud
What you will do:
- Take the dish and pour some milk into it.
- Now drop a few drops of colouring agents in the middle.
- Now take an earbud soaked in liquid dish soap and dip it into the middle of the food colouring.
- Watch the colours get scattered in all directions like fireworks!
Conclusion
Adding soap to the milk weakens its surface tension by pushing the milk molecules. The food coloring is pushed along with them which causes the spectacular sight of fireworks on liquids!
Activity 2
What you will need:
1 glass containing water
1 paper clip
1 piece of tissue paper
1 ear bud
A small quantity of liquid soap
What you will do:
- Take the paper clip and try and balance it on top of the water surface of the glass
- If it sinks, take it out from the glass
- Now, place the piece of small tissue paper on the water surface and then put the paper clip on it
- Next, gently remove the tissue paper from beneath the paper clip as it will start floating on the water surface
- Dip the ear bud in liquid soap and touch its tip into the water
- The paper clip will again sink at the bottom!
Conclusion
When you tried to float the paper clip, it sinks because the metal with which the clip is made is denser than the water. However, when placing it on a piece of floating tissue paper, it does not sink because now the surface tension of the water is supporting it.
Again, when you touch the water with soap, this surface tension gets reduced. So, the clip sinks like a brick into the glass.
-
