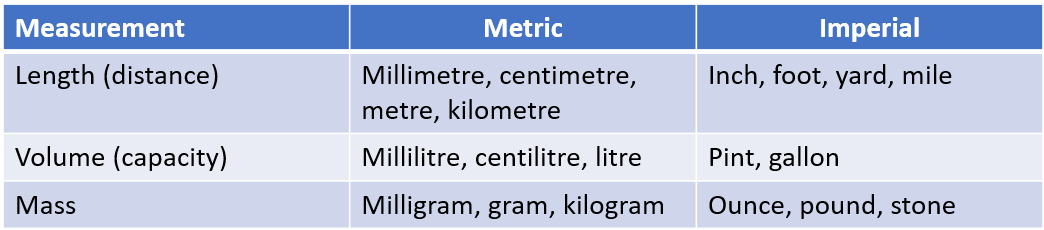
Converting units
 Mustafa is planning to run a 5 km race. In order to prepare for the race, he has been running each day. At the end of the first week, he runs 575 m without stopping. He tries to figure out how that translates in kilometres so he converts 575 metres to kilometres. How many kilometres are equal to 575 metres?
Mustafa is planning to run a 5 km race. In order to prepare for the race, he has been running each day. At the end of the first week, he runs 575 m without stopping. He tries to figure out how that translates in kilometres so he converts 575 metres to kilometres. How many kilometres are equal to 575 metres?
Sometimes when you convert metric units you don’t have a whole number answer. When this happens, you end up with an answer that is a decimal.
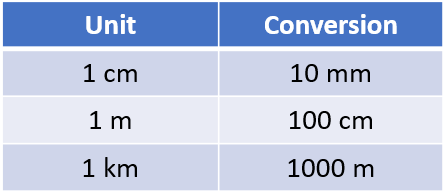
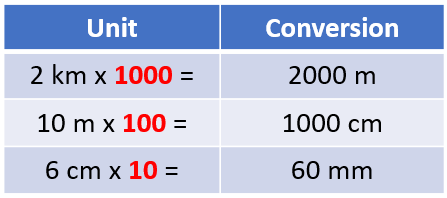
We said earlier that:
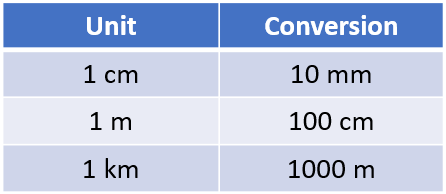
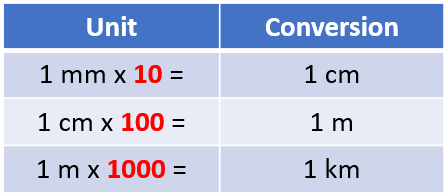
But what happens if we aren't working in numbers rounded like the above? Let's explain this by way of example:
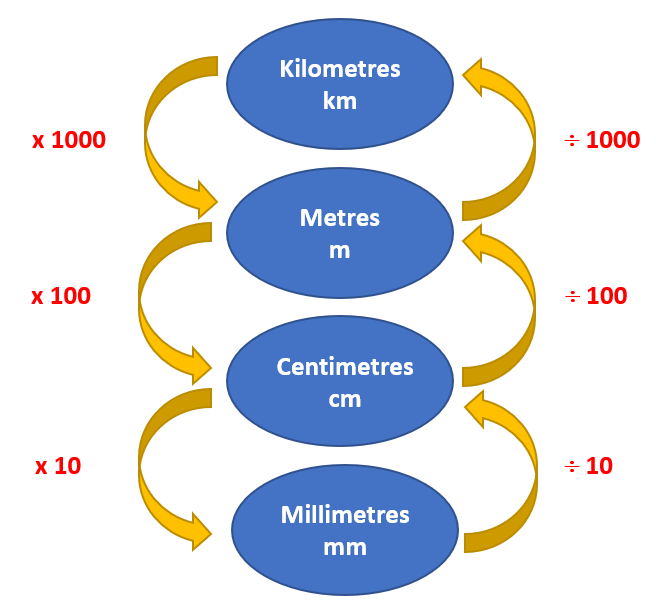
- 1 mm = ? cm
- Since you are converting a smaller unit to a larger unit, you are going to divide. There are 10 mm in one centimetre, so you are going to divide 1 by 10. You are dividing 1 whole into 10 parts
- 1 mm = (1 ÷ 10) cm
- 1 mm = 0.1 cm
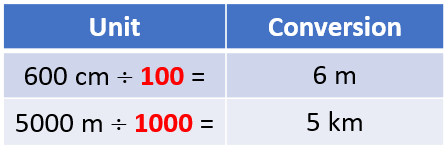
The same principle will apply when converting cm to m:
- 1 cm = (1 ÷ 100) m
- 1 cm = 0.01 m
...and m to km:
- 1 m = (1 ÷ 1000) km
- 1 m = 0.001 km
Let's now go back to the word problem about Mustafa and his race preparation!
- What is 575 m in km?
- 575 m ÷ 1000 = 0.575 km
- Mustafa can run 0.575 km without stopping. He has a way to go before he can run the full 5 km without stopping!


 Mustafa is planning to run a 5 km race. In order to prepare for the race, he has been running each day. At the end of the first week, he runs 575 m without stopping. He tries to figure out how that translates in kilometres so he converts 575 metres to kilometres. How many kilometres are equal to 575 metres?
Mustafa is planning to run a 5 km race. In order to prepare for the race, he has been running each day. At the end of the first week, he runs 575 m without stopping. He tries to figure out how that translates in kilometres so he converts 575 metres to kilometres. How many kilometres are equal to 575 metres?