Sectieoverzicht
-
-
States of matter refers to the different forms in which a matter can exist. In broader terms, there are four different states of matter namely solid, liquid, gas, and plasma. Matter in different states exhibit distinct physical and chemical properties. While a matter in a solid has a fixed volume and shape, it loses its shape in liquid form, but its volume remains the same. In gaseous state, both the volume and shape are not fixed.
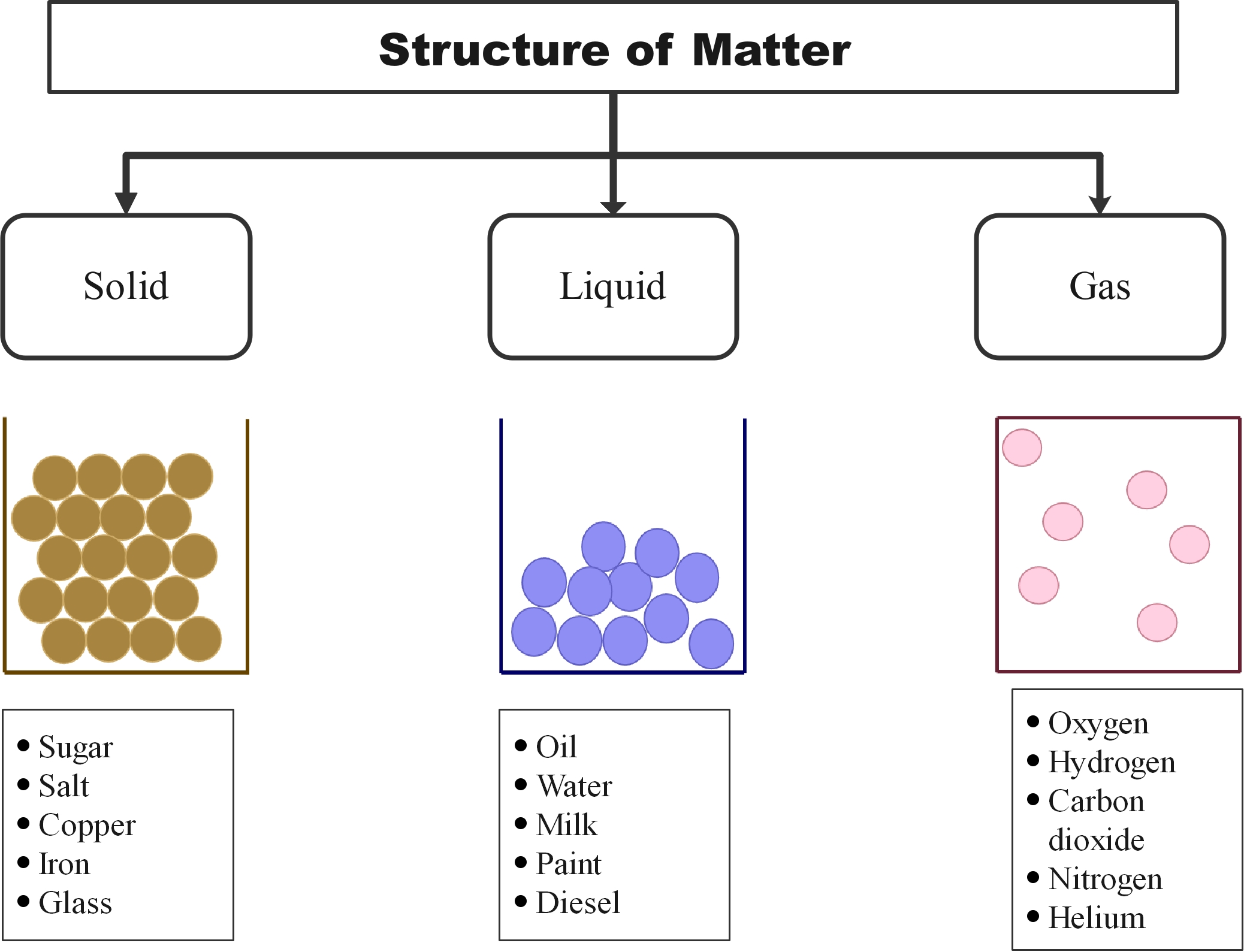
Figure 1: The three states of matter
Solids
The particles in a solid:
- sit very closely together.
- are in a regular arrangement and in fixed position.
- vibrate about a fixed position but do not move through the solid.
- are held together by strong forces.
This explains why solids have a fixed shape and volume.
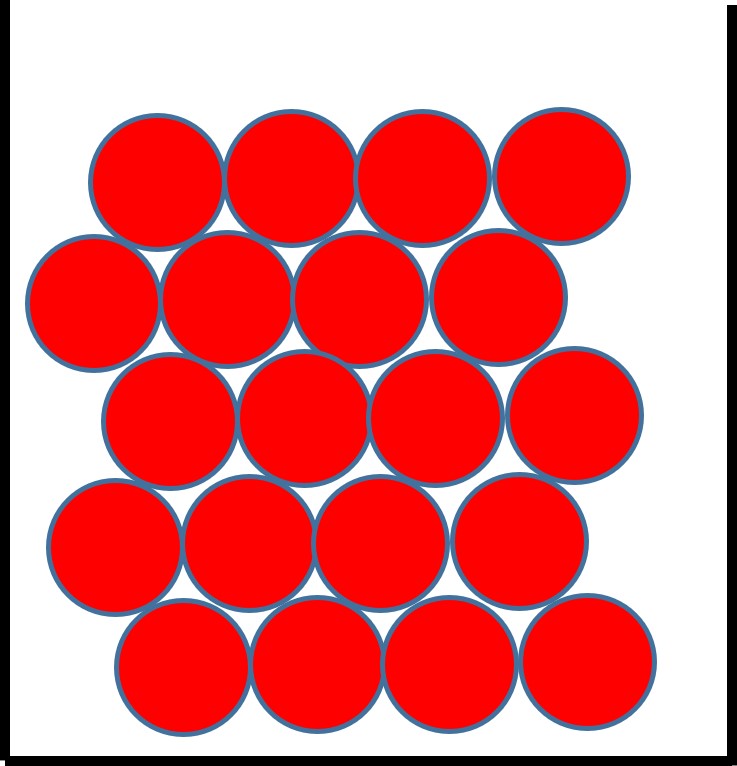
Figure 2: the particle arrangement in a solid
Liquids
The particles in a liquid:
- sit close together but have some gaps.
- can move past each other because of the gaps.
- have enough energy to prevent the forces between them holding them in a fixed, regular arrangement.
- are randomly arranged.
This explains why liquids have a fixed volume but take on the shape of their container.
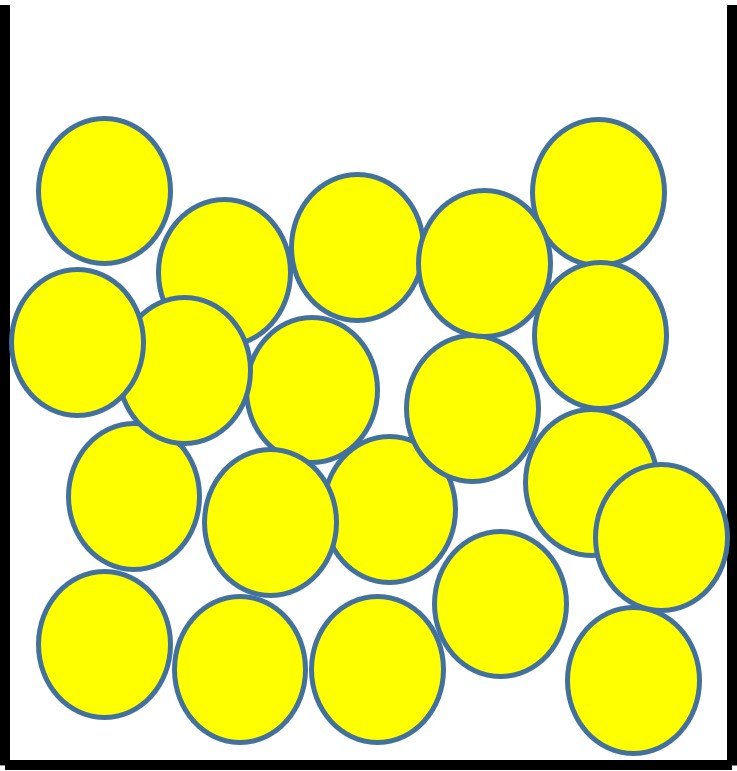
Figure 3: the particle arrangement in a liquid
GasesThe particles in a gas:
- are much further apart than in a solid or liquid.
- are entirely free to move because the forces between them are weak.
- are randomly arranged.
- move quickly and randomly in all directions.
This explains why gases completely fill their container and have the same volume as their container.
Figure 4: the particle arrangement of a gas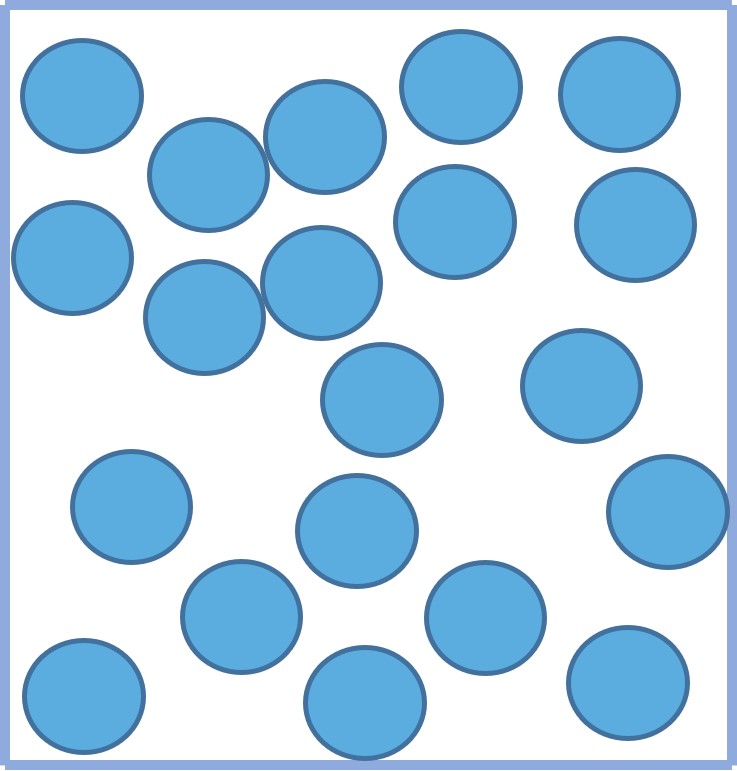
-
