Sectieoverzicht
-
-
STI's and STD's
Sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) begin as sexually transmitted infections (STIs). Infection occurs when a sexually transmitted bacteria, virus, or other microbe enters the body and begins multiplying. Once established, the infection may progress into a disease an STD.
Common STI's include gonorrhea and syphilis which have previously been discussed.
Others which are very common are:
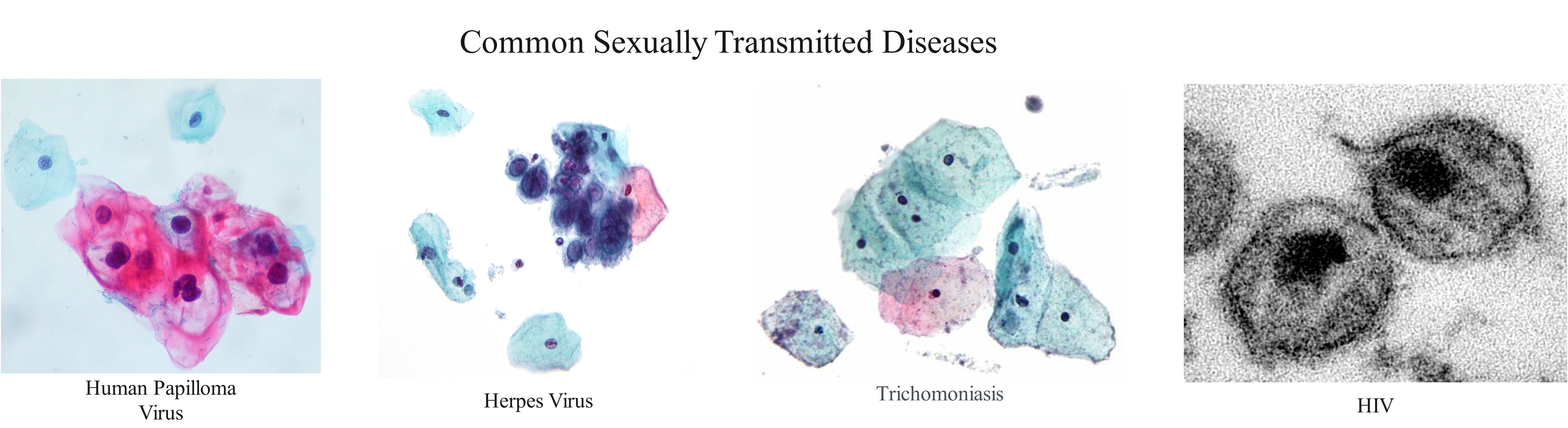
Image: Emma Harrage. CC BY
HPV: Human Papillomavirus or HPV is a group of viruses that can lead to warts, genital warts or even cancer. Most HPV types do not cause damage to human body and clear up shortly after infection. Sexually active individuals are in danger of becoming infected with every second person having it at some point of life. Young people are encouraged to take HPV vaccines, preventing from dangerous types of the virus, while women are recommended to have regular Pap smear tests.
Credit: TED-ed. The most common STI in the world
Chlamydia: One of the most widespread sexually transmitted infections, Chlamydia can lead to serious complications if not treated timely. The infection affects mainly women and some may have no symptoms at all.
In other cases, the infected person may experience abnormal vaginal discharge or urinating discomfort. It is important to locate and take measures as soon as possible before Chlamydia damages the uterus, fallopian tubes, reproductive system, which may end in infertility.
Herpes: Herpes is one of the most common diseases transmitted through all types of sexual contact as well as simple touching. Oral herpes can cause blisters or cold sores on the lips, on or inside the mouth. Genital herpes can involve sores, blisters, itching in genital area or even urinating problems. However, most of the times the virus shows no symptoms at all and a person can be unaware of it.
There are medicines keeping herpes symptoms subdued and limiting transmission. However, once in your body, there is no cure to get rid of it.
Trichomoniasis is caused by a microscopic, one-celled parasite called Trichomonas vaginalis. This organism spreads during sexual intercourse with someone who already has the infection.
The organism usually infects the urinary tract in men, but often causes no symptoms. Trichomoniasis typically infects the vagina in women. When trichomoniasis causes symptoms, they may appear within five to 28 days of exposure and range from mild irritation to severe inflammation.
HIV: Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) is a virus that attacks and destroys the body’s T lymphocytes. The reduction in the number of T lymphocytes in the body due to HIV can then lead to the development of Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome (AIDS). Individuals with AIDS have a weakened immune system and so are more vulnerable to opportunistic infections.
Prevention and treatment
There are several ways to protect yourself against catching an STD:
- Abstinence - The most reliable way to avoid infection is to not have sex (i.e., anal, vaginal or oral).
- Vaccination - Vaccines are safe, effective, and recommended ways to prevent hepatitis B and HPV. HPV vaccination is recommended for preteens ages 11 or 12 up to age 26, if not vaccinated already. You should also get vaccinated for hepatitis B if you were not vaccinated when you were younger.
- Reduce Number of Sex Partners - Reducing your number of sex partners can decrease your risk for STDs. It is still important that you and your partner get tested, and that you share your test results with one another.
- Mutual Monogamy - Mutual monogamy means that you agree to be sexually active with only one person, who has agreed to be sexually active only with you. Being in a long-term mutually monogamous relationship with an uninfected partner is one of the most reliable ways to avoid STDs. But you must both be certain you are not infected with STDs. It is important to have an open and honest conversation with your partner.
- Use Condoms - Correct and consistent use of the male latex condom is highly effective in reducing STD transmission. Use a condom every time you have anal, vaginal, or oral sex.
STDs/STIs caused by bacteria or parasites can be treated with antibiotics. The treatments, complications, and outcomes for viral STIs depend on the virus. Treatments can reduce the symptoms and the progression of most of these infections but not cure them.
Credit: Medical Centric. Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDs), Causes, Signs and Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment.
-
