Sectieoverzicht
-
Archimedes principle states that an object completely submerged in a fluid (any liquid) experiences a force pushing upward called the buoyant force, which is equal to the volume of the fluid that the body displaces. This is also called the law of buoyancy. If an object weighs more than its own volume in fluid, it will sink.
This principle is illustrated in the graphic below.
Archimedes' principle allows the buoyancy of any floating object partially or fully immersed in a fluid to be calculated. Understanding buoyancy is important for finding out how objects behave in a fluid (liquid or gas).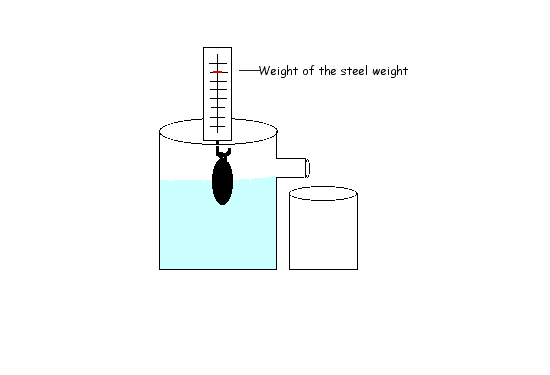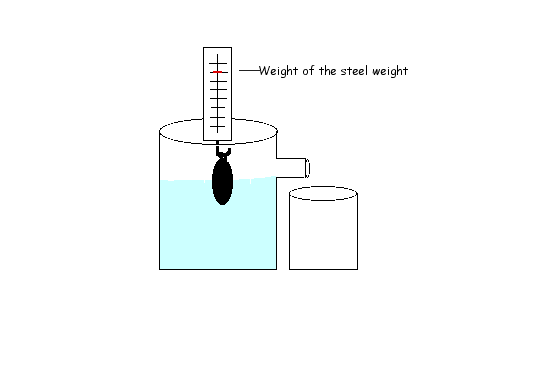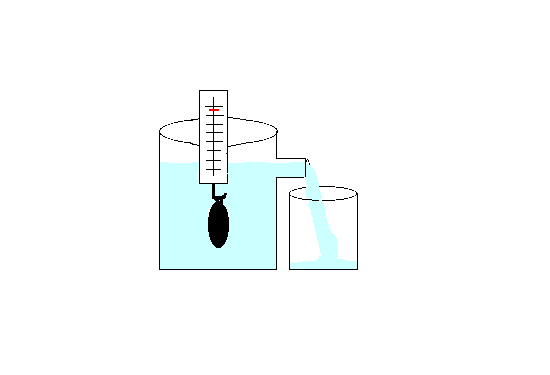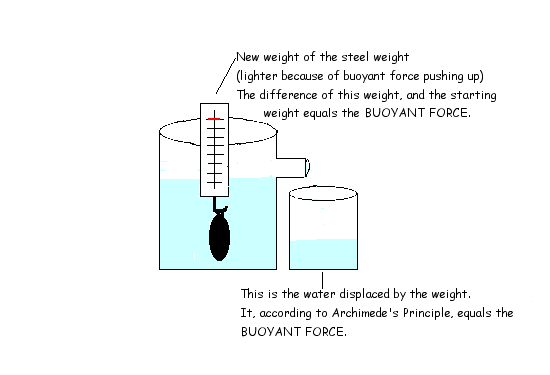
Due to the buoyancy force acting on objects in water, the object will weigh less in water. The buoyant force pushes upward against the object while gravity pushes downward.
-
Experimenting with Archimedes principle
What you will need:
- Two eggs (or grapes)
- Two glasses of water
- Salt
- A spoon
What you will do:- Place one of the eggs into one of the glasses of water. What do you notice?
- Put a teaspoon of salt into the other glass of water and stir until it dissolves.
- Place the other egg into the salty water. What do you notice and why?
What did you find?- When you place an egg into a normal glass of water it will sink. This is because the egg has a greater density than the water.
- When you put an egg into salty water it floats. The salt increases the density of the water, which makes the buoyancy stronger and makes the egg feel lighter. The egg floats in salty water because the water now has a greater density than the egg.
-
Calculating Buoyant force
-
