Sectieoverzicht
-
-
Multicellular animals and plants consist of different types of cells organised in a hierarchy as tissues, organs, and systems.
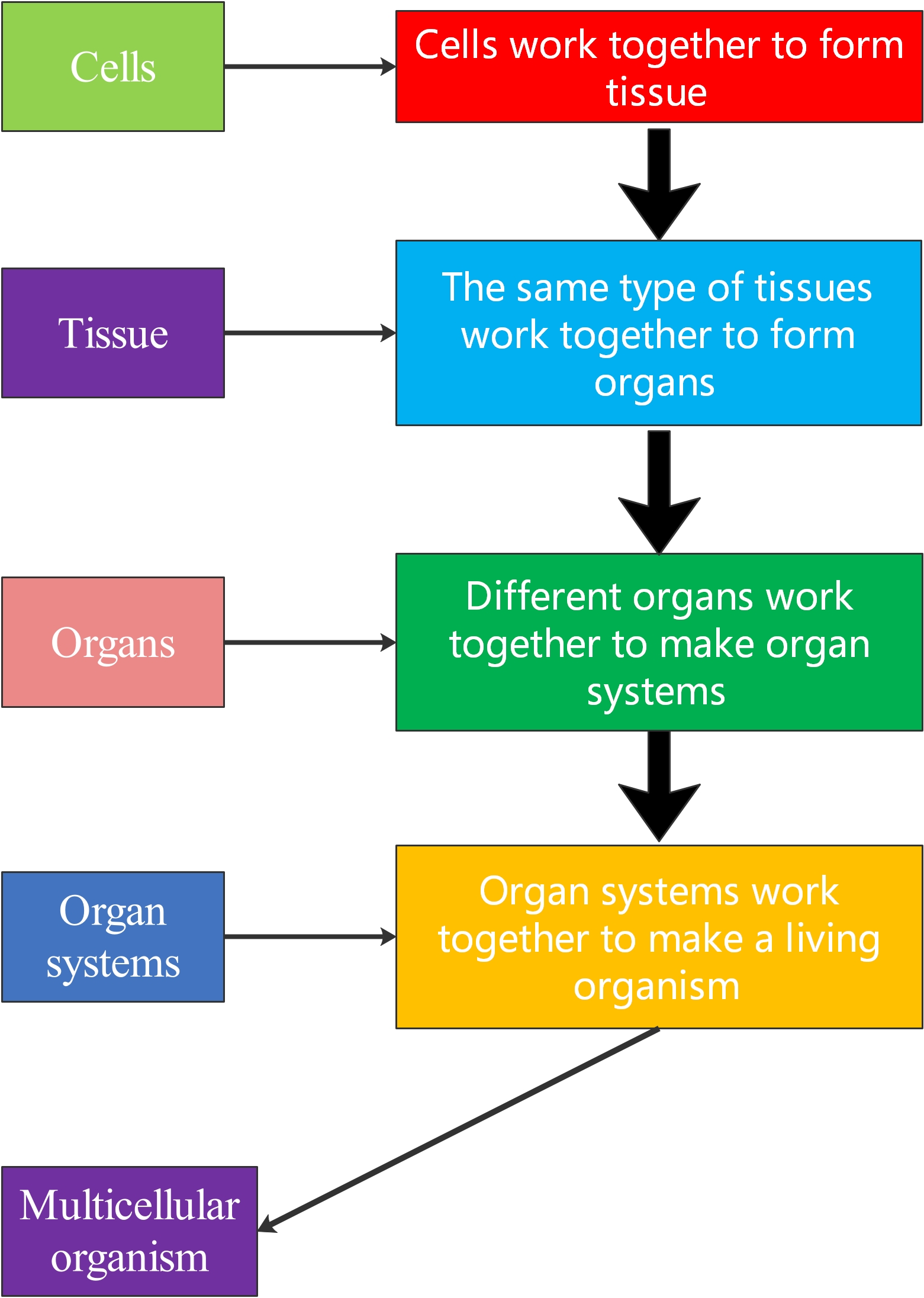
Image: Emma Harrage. CC BY
Cells: Cells are the smallest unit of life. Most cells have features which give them different functions within an organism.
The term tissue is used to describe a group of cells that are similar in structure and perform a specific function.
Tissues: A group of similar cells in the same place with the same function is a tissue.
Plants: In plants, dermal tissue covers the leaves, fruits, flowers, roots, and stems of plants. Dermal tissue stops the plant from losing too much water.
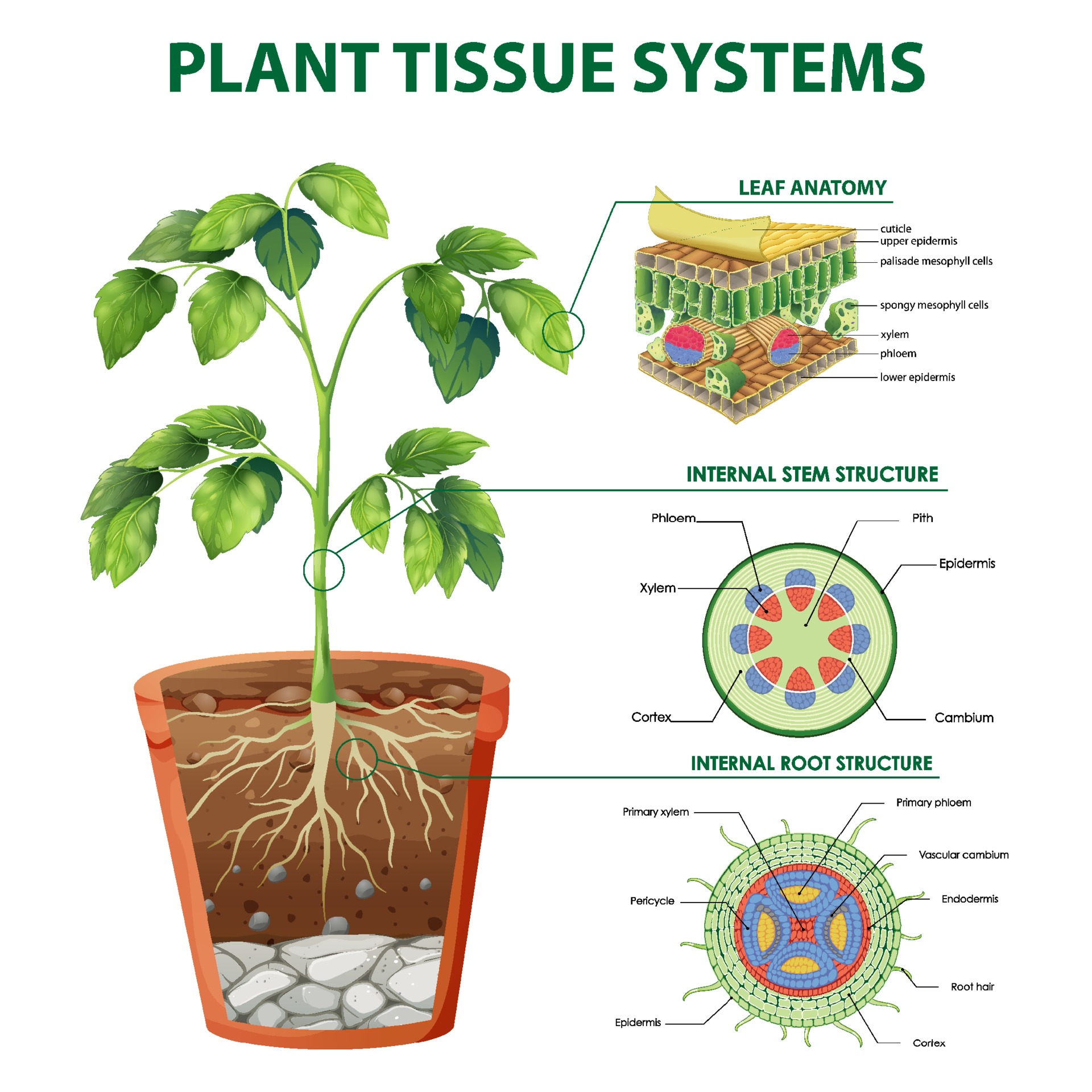
Image: Vecteezy.com. Public domain
Animals: Examples of tissues in animals include muscle tissue and nerve tissue.
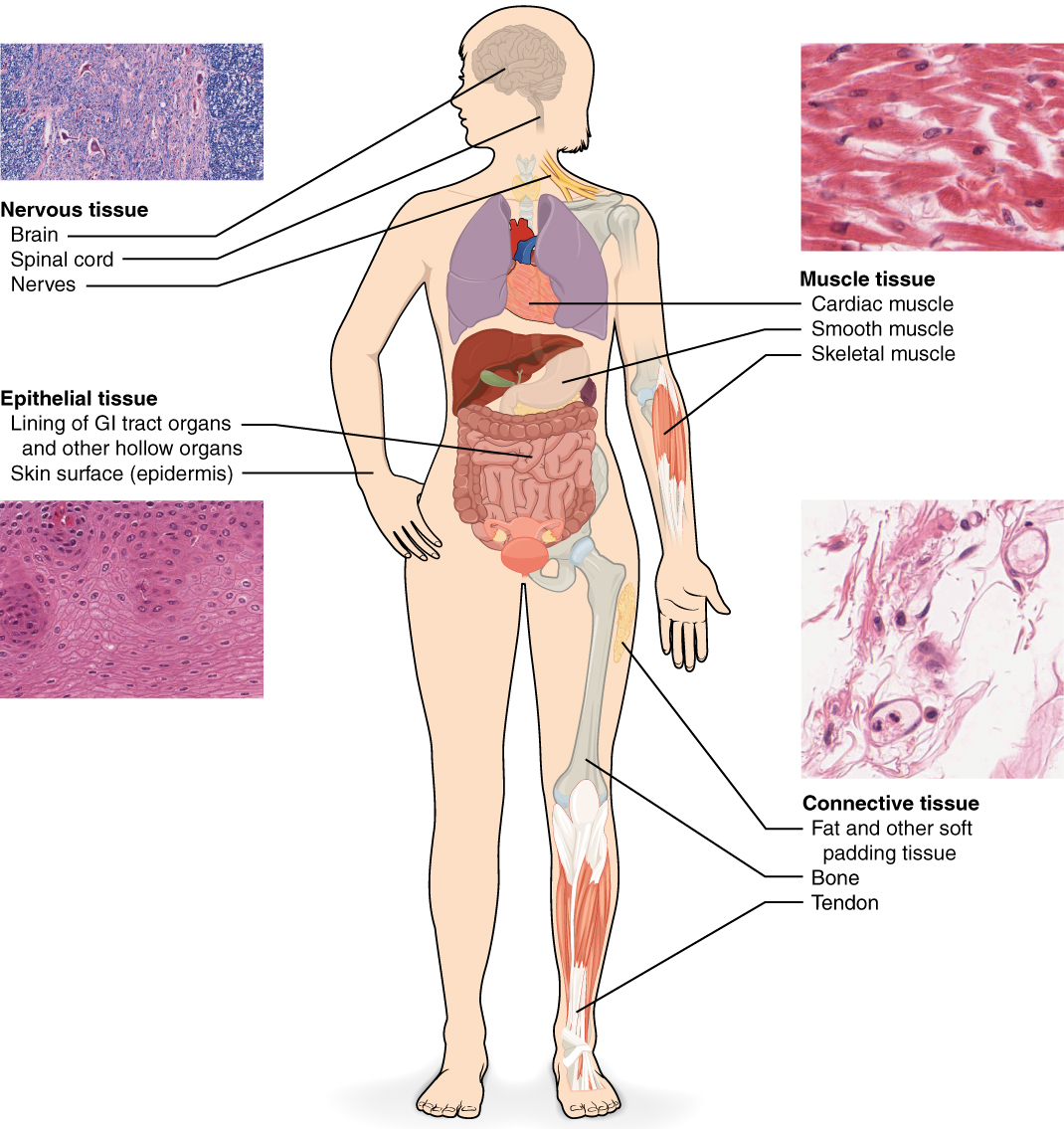
Image: Oregon State University. CCA 4.0
Muscle tissue: made of muscle cells that can contract and relax to move parts of the body.
Nerve tissue: made of nerves, found in the brain and spinal cord, and the network of nerves that spreads throughout the body. It sends electrical signals to control and coordinate actions.
Plants: Roots are plant organs. They keep plants securely in the ground and are covered with root hair cells which absorb water and nutrients from the soil. Other plant organs are leaves, stems and flowers.Organs: A group of tissues in the same place with the same function is an organ.
Image: CK12.org. CK-12 License
Animals: The heart is an organ made from muscle and nerve tissue and pumps blood around the body. Other examples of animal organs include the liver, brain, lungs, stomach, intestines, kidneys, bladder, and skin.Image: Vecteezy.com. Public domain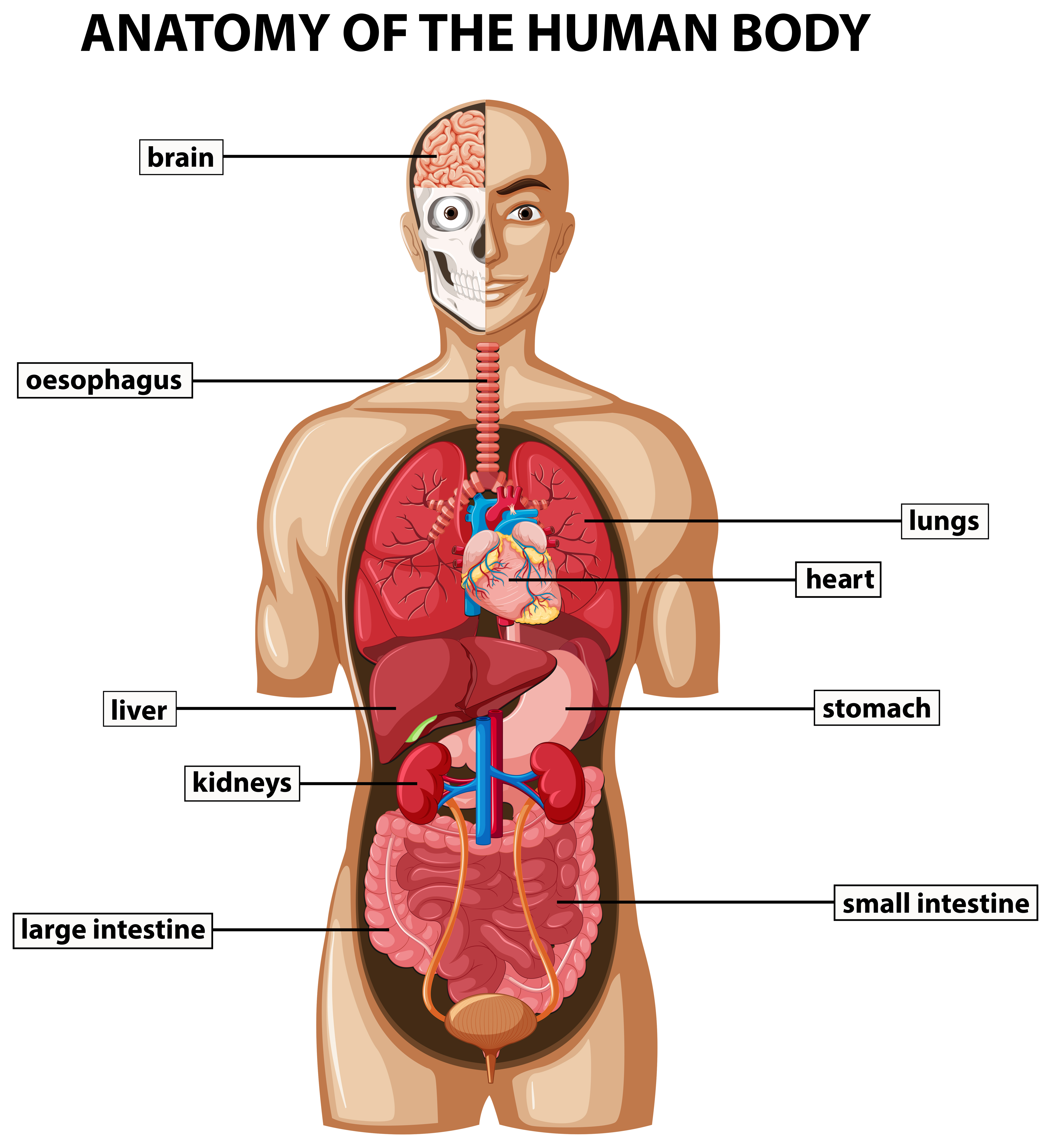
The human body contains five organs that are considered vital for survival. They are the heart, brain, kidneys, liver, and lungs. If any of the five vital organs stops functioning, the death of the organism is imminent without medical help.
The heart is in the center of the chest, and its function is to keep blood flowing through the body. Blood carries substances to cells that they need and carries away wastes from cells.
The brain is in the head and functions as the body’s control center. It is the seat of all thoughts, memories, perceptions, and feelings.
The two kidneys are in the back of the abdomen on either side of the body. Their function is to filter blood and form urine, which is excreted from the body.
The liver is located on the right side of the abdomen. It has many functions, including filtering blood, secreting bile that is needed for digestion, and producing proteins necessary for blood clotting.
The two lungs are located on either side of the upper chest. Their main function is exchanging oxygen and carbon dioxide with the blood.
Your skin is your largest organ and plays a vital role in detecting hot and cold, regulating your body temperature, and protecting your muscles, bones and internal organs from outside infection and disease.
Here are some interesting facts about your skin:
- The average person’s skin covers an area of 2 square meters.
- The average adult has approximately 4 kg's of skin which contains 18 km of blood vessels.
- The average person has about 300 million skin cells. A 6.5 square centimetre of skin has about 19 million cells and up to 300 sweat glands.
Plants: Plants have two organ systems.Organ systems: Two or more organs with the same function is an organ system.
The shoot organ system in a plant is made from leaves, stems, buds, fruits, and flowers.
The root organ system of most plants are all the parts that are underground.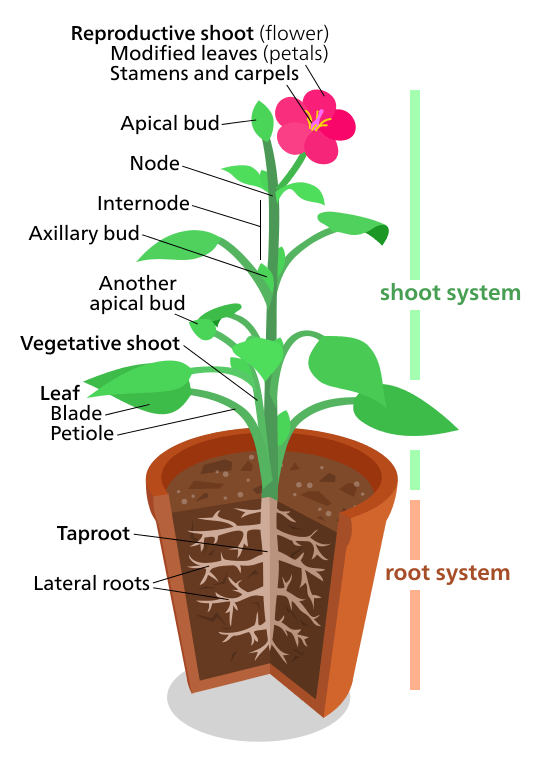
Image: Kelvinsong. CC BY SA 3.0
Animals: There are 11 organ systems in the human body that each have a different function.
Here are some examples:Organ system
Main tissues and organs
Function
Circulatory. The circulatory system circulates the blood in the body.
Blood, blood vessels like the arteries, veins, capillaries, and heart.
Transports substances in the blood around the body.
Maintenance of uniform temperature,
Supply of oxygen and nutrition to all the cells and tissues
Collection of waste matter and transport it to the urinary system.
Respiratory. The respiratory system helps in gaseous exchange
Nose, larynx, bronchi, and lungs.
Takes in oxygen, removes carbon dioxide
Digestive. This system is meant to break down the food and absorb nutrients into the blood circulation.
Mouth, teeth, oesophagus, stomach, liver, pancreas, intestine, rectum, and anus.
Breaks down food, absorbs nutrients
Musculoskeletal system.
This system provides support and movement.
Muscles. Bones.
Responsible for the movements of the body.
They provide the body with a proper shape, frame, and support for the organs.
Nervous system.
This is called the master body system, as it controls all the other organ systems of the body.
Brain, spinal cord, and nerves.
The nervous system regulates whole-body functions, and movements.
It stimulates the release of hormones when needed to control other systems.
It regulates body movements through muscles and controls respiration, heartbeat, digestion, urination etc.
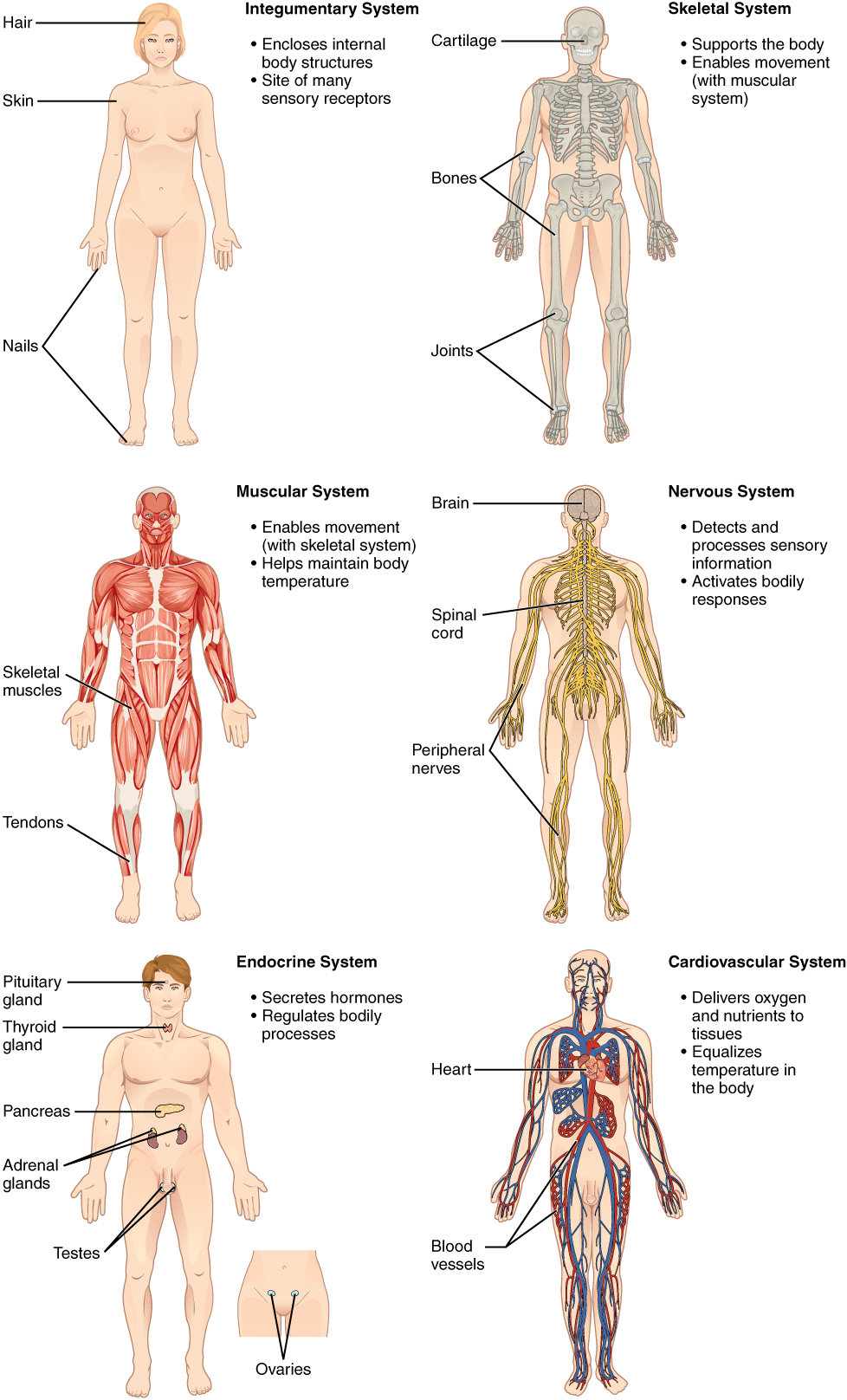
Image: Human Biology. CCA NC 4.0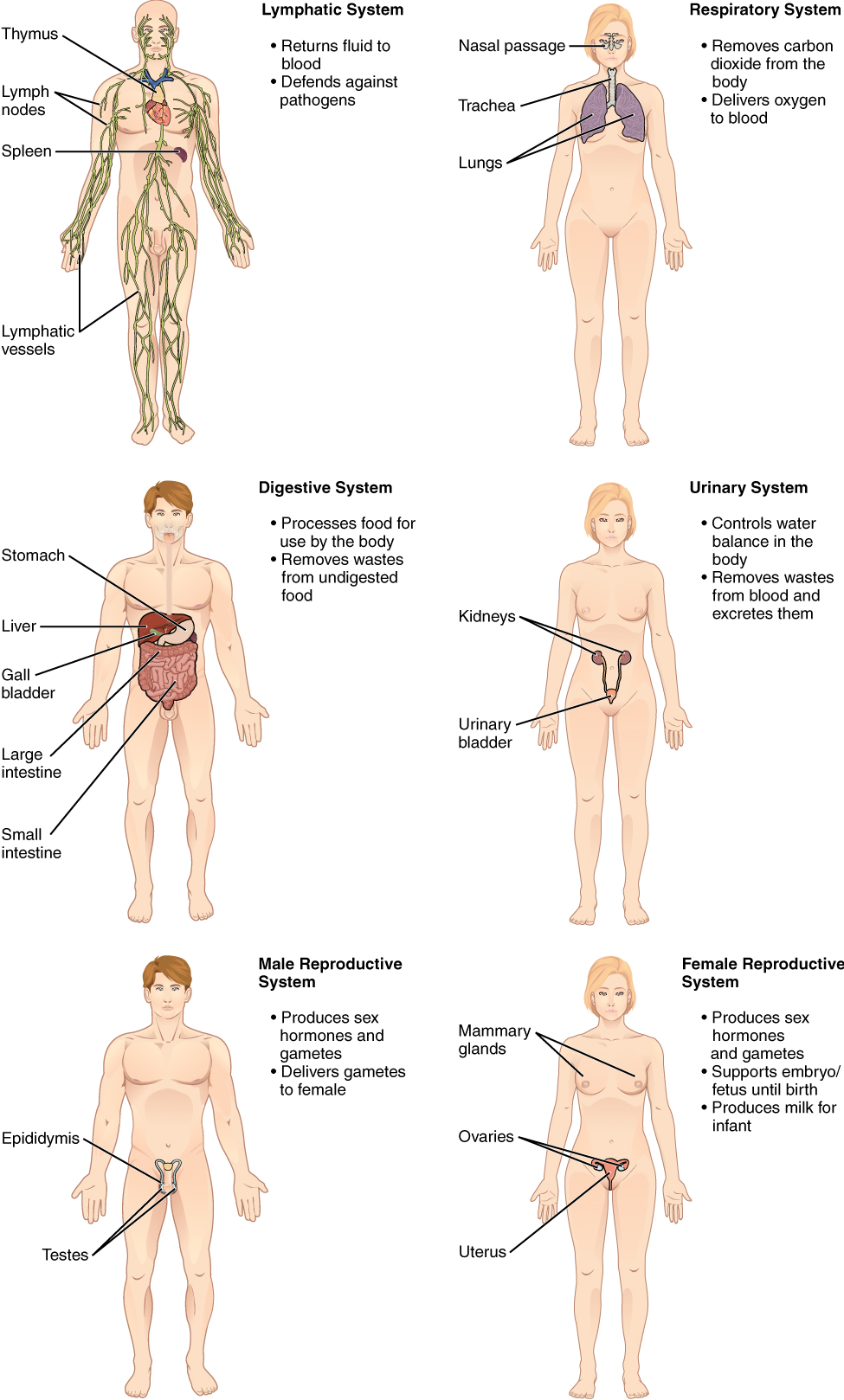
Image: Human Biology. CCA NC 4.0
Credit: Fuse Schools - Global Education
-
