Sectieoverzicht
-
-
What are cells?
All life on Earth is made from cells. Without cells, there can be no life.
Almost all cells are so small that you need a microscope to see them. Some organisms, like bacteria are made of only one cell. These are unicellular organisms.
Others, like trees and blue whales, are made from millions or even billions of cells. These are multicellular organisms.
Cells are the basic, fundamental unit of life. So, if we were to break apart an organism to the cellular level, the smallest independent component that we would find would be the cell.
Animals and plants are multicellular organisms – they consist of many cells that work together. A living thing, whether made of one cell (like bacteria) or many cells (like a human), is called an organism. So, cells are the basic building blocks of all organisms.
Animal cell structure
The main parts of an animal cell are the nucleus, cell membrane, cytoplasm, and mitochondria.
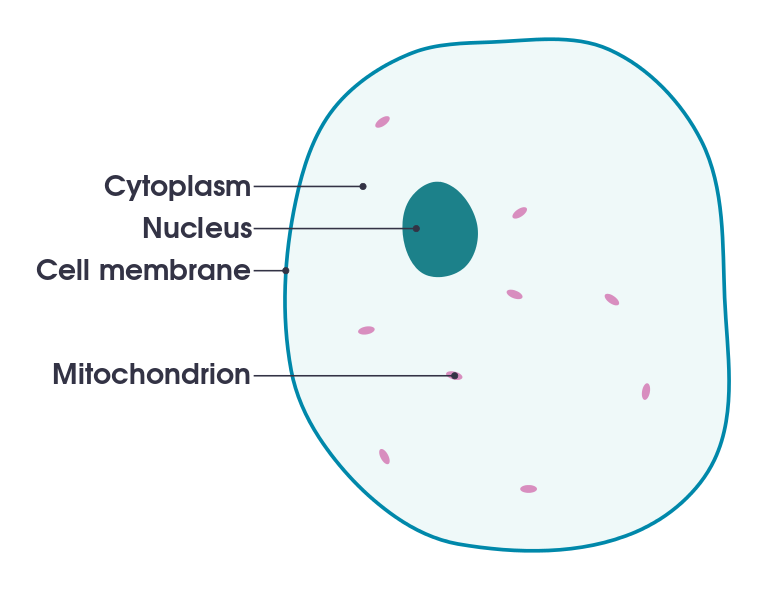
Figure 1: A simple diagram of an animal cell. Image: domdomegg. (2016). CCA 4.0
Plant cell structure
Plant cells contain the same features as animal cells. They also have some additional ones:
- chloroplasts
- cell wall made of cellulose
- large central vacuole
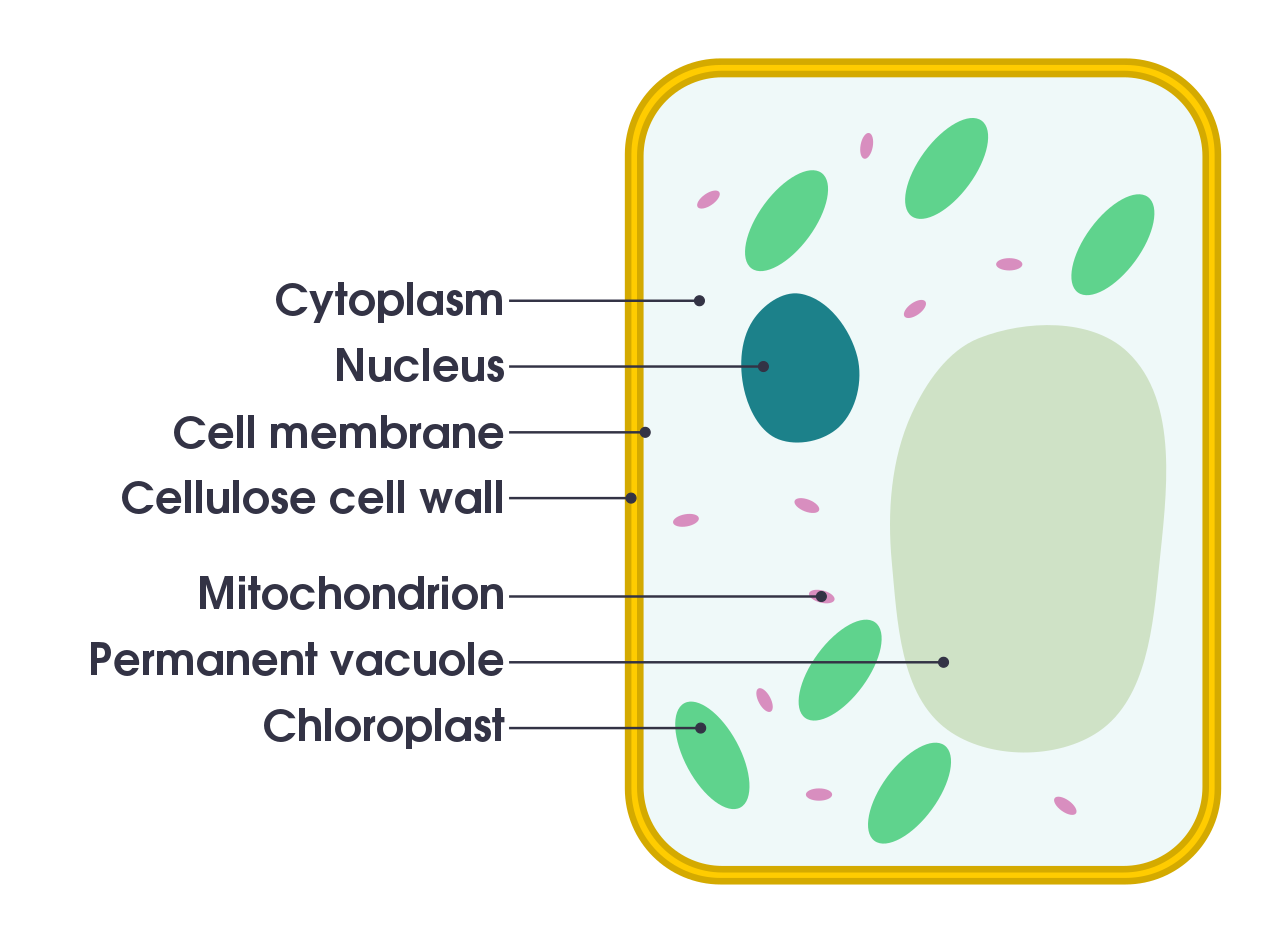
Figure 2: A simple diagram of a plant cell. Image: domdomegg. (2016). CCA 4.0
What's in a cell?
Cells are the basic building blocks of all animals and plants.
Inside cells are various structures that are specialised to carry out a particular function. Both animal and plant cells have these components:
- Cell membrane – this surrounds the cell and allows nutrients to enter and waste to leave it.
- Nucleus – this controls what happens in the cell. It contains DNA, the genetic information that cells need to grow and reproduce.
- Cytoplasm – this is a jelly-like substance in which chemical reactions happen.
- Mitochondria – these are the powerhouse of the cell. They are structures where respiration takes place.
How are plant and animal cells different?
Plant cells have all the parts in the list above, plus a few extra structures:
- Cell wall - this is an outer structure that surrounds the cell and gives it support.
- Vacuole - this is a space within the cytoplasm of plant cells that contains sap.
- Chloroplasts - these contain chlorophyll and are the site of photosynthesis.
Summary of features found in cells and their functions:
Cells are too small to be seen by the naked eye. To see them you would need to use a microscope.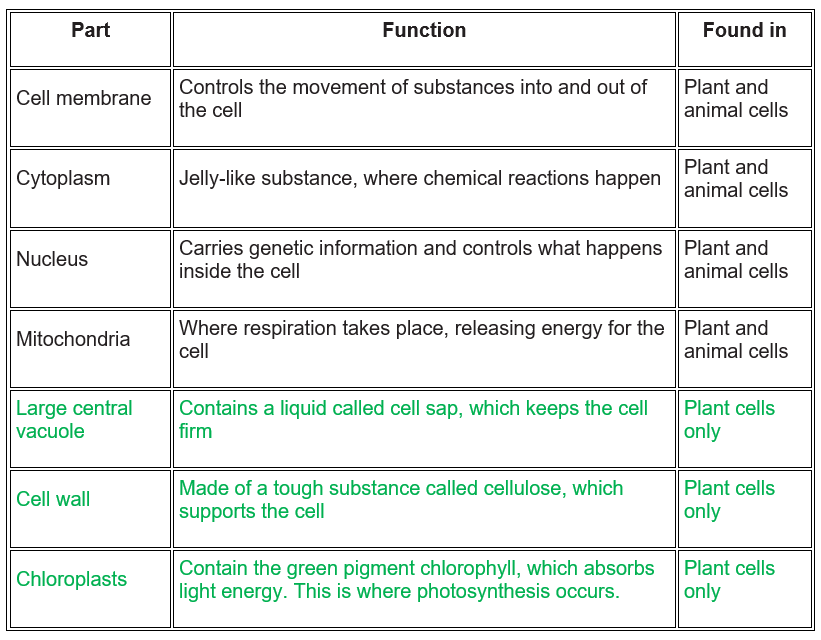
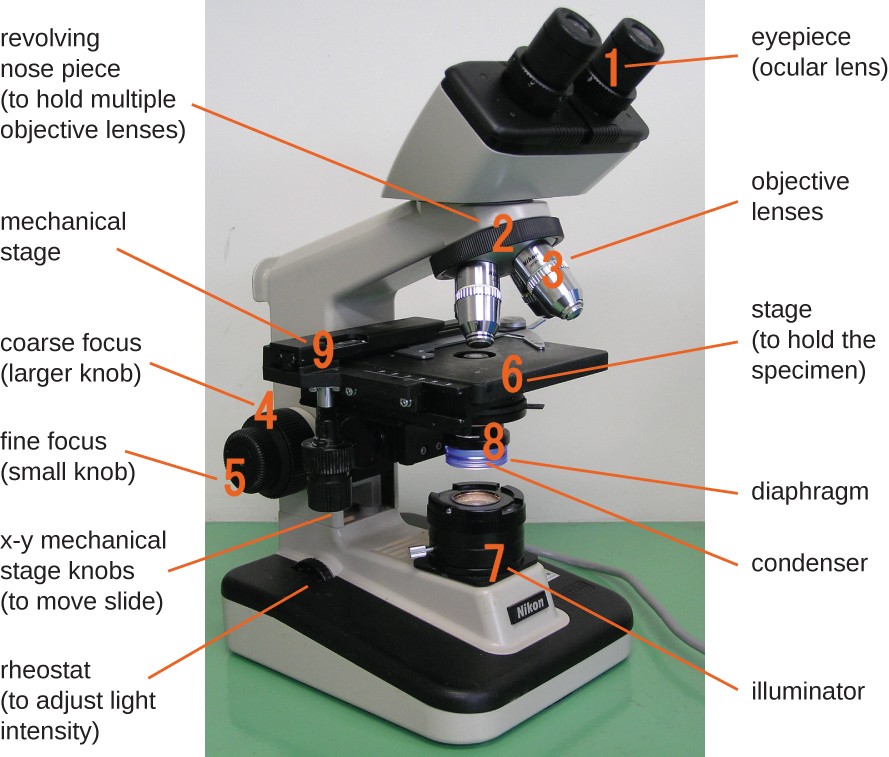
Image: OpenStax. CC BY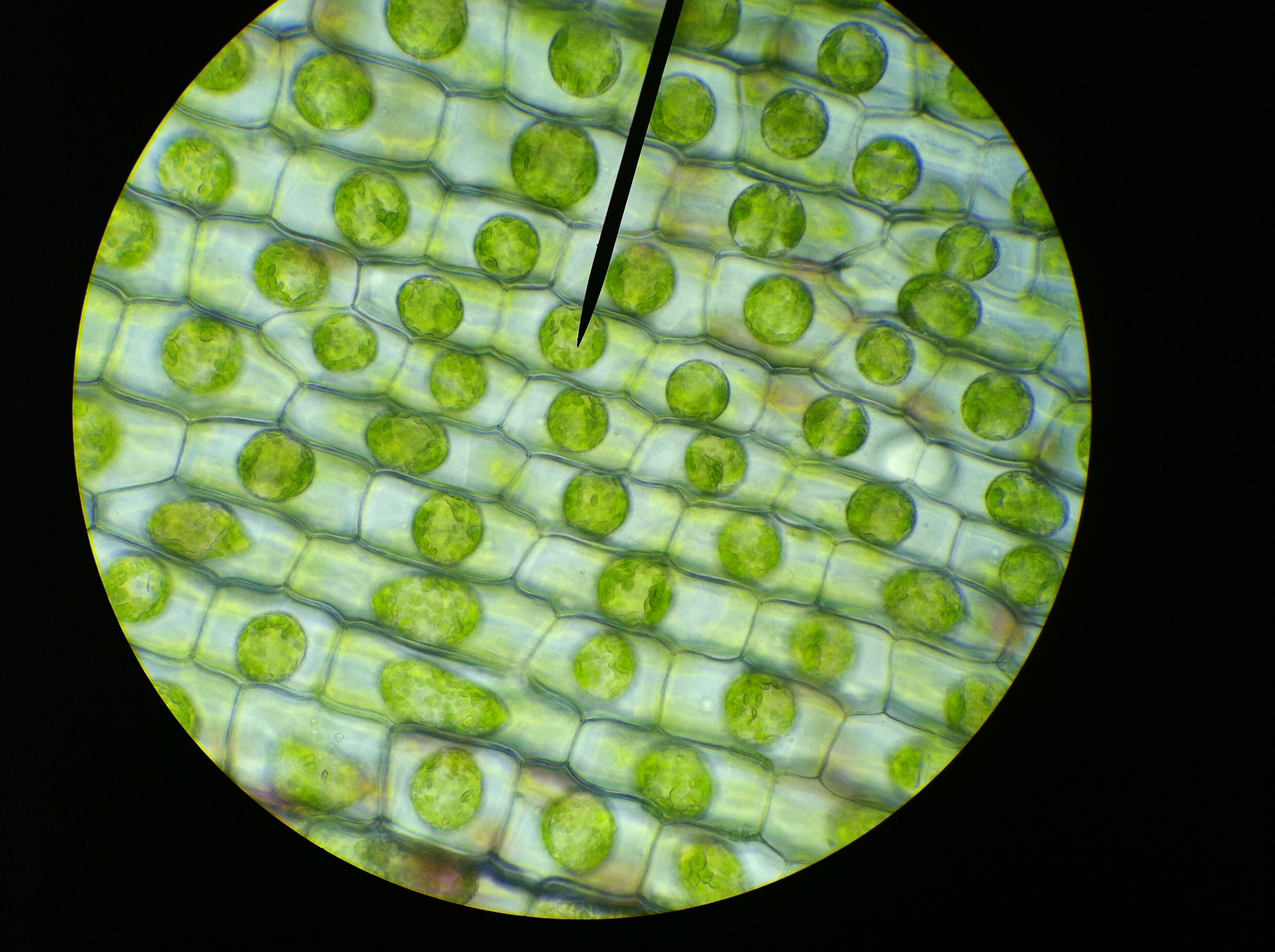
Figure 3: Plant cells under a microscope. The bright green blobs you can see are the nucleus of each cell. You can also see the cell wall. Image: fickleandfreckled. CC BY 2.0
Credit: Fuse Schools- Global Education. Introduction to Cells.
-
