Section outline
-
-
Scientists often make measurements. These need to be stated with the units of the quantity being measured, and the accuracy of the measurements.
Measurement is the process of finding the length, size, or quantity of a substance. Since ancient times, people have used several ways to measure length. A physical quantity (like length) has to be measured with respect to some fixed quantity.
A fixed quantity with respect to which a physical quantity is measured is called a unit. A unit is used as a standard of measurement. In early times, people used different body parts like hand span, cubit, and fathom to measure length.
Foot, pace, and yard are some other units of length based on body parts. However, these units are not reliable as the length of body parts varies from person to person. Therefore, people realised the need for standard units of measurement.
Standard Units of Measurement
Standard Units of Measurements Units that have a fixed quantity and do not vary from person to person and place to place are called standard units. For example, the metric system, created by the French in 1790, is a standard set of units.
Adopting standard units of measurement does not solve the problem. People in different countries may be using a different set of standard measurement units. For the sake of uniformity, scientists all over the world have adopted a common set of units. This system is called the International System of Units or the SI units. The adoption of SI units in 1960 made it easier for scientists of different countries to communicate their results to one another.
The SI unit of length is metre. Some common standard units of length are inch, millimetre, centimetre, and kilometre.
Depending on the size of the object, we need to measure, we have to choose an appropriate unit.
For example, we use metres to measure the length of a piece of cloth, kilometres to measure the distance from one place to another, millimetres to measure the thickness of the hair, and so on. Centimetre (cm) and millimetre (mm) are used to measure shorter distances while kilometre (km) is used to measure longer distances.
One kilometre is divided into 1000 equal divisions, each called metre. One metre is divided into 100 equal divisions, each called centimetre which is again divided into equal divisions. Each division is called millimetre.
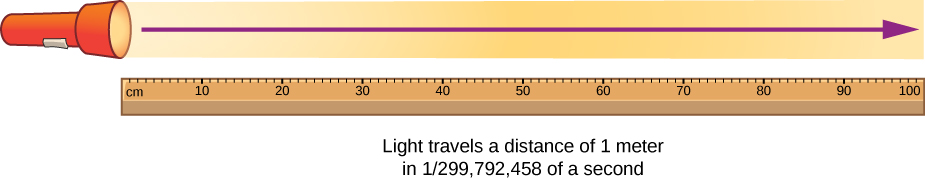
The meter is defined as the distance light travels in 1/299 792 458 of a second.
Commonly used units of length:
10 millimetres = 1 centimetre (cm)
100 centimetres = 1 metre (m)
1000 metres = 1 kilometre (km)
A unit can be converted to another. Here is an example.
Example 1: Raju and his friend Akhil live 2000 m from each other. Express the distance between their houses in kilometres (km).
Solution: We know that 1000 m = 1 km
Therefore, 2000 m = 2 km
Therefore, the distance between the two houses is 2 km.
Time - in physics time is measured in seconds (s). You can count seconds by saying at a steady rate one thousand, two thousand, three thousand. However, for accuracy when doing an experiment, you should always use a stopwatch.
Mass
If you buy a bag of sugar at the shops, you will see the mass of the sugar marked on the bag. It will be written in grams (g) or kilograms (kg). Kilo always means a thousand.
1 kg = 1 000 grams.
When you are measuring it is important to use appropriate and sensitive equipment to ensure your measurements are accurate.
If you were measuring the length of a soccer field, would it be appropriate to use a 15 cm ruler or the measuring wheel? It you were measuring the length of a stone; would you use the tape measure or the Verner calipers?
If you were measuring the time it took a classmate to run 100 m would you use a stopwatch or the clock on your classroom wall?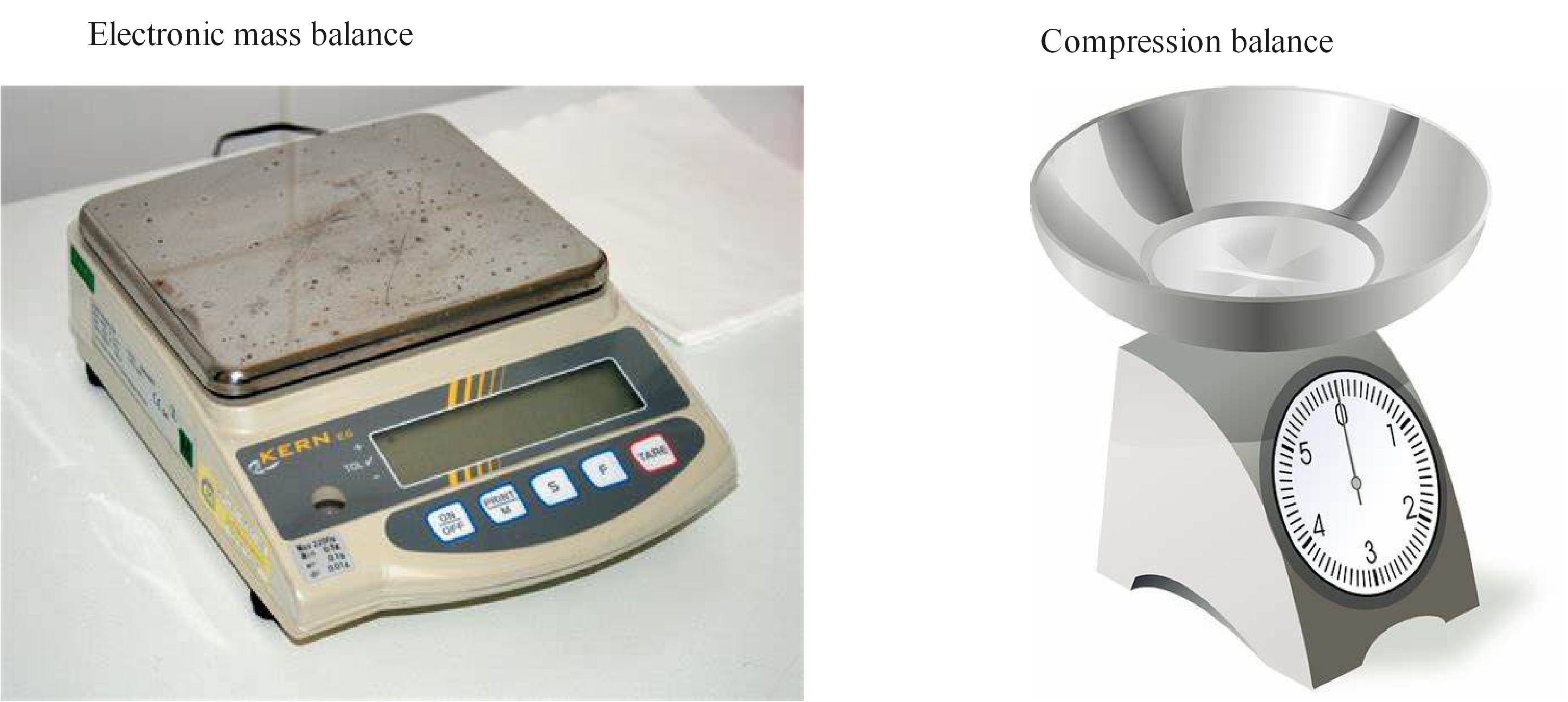
If you needed to measure 5 g of sugar, the more appropriate balance to use would be the electric mass balance. This is because they are very sensitive balances and will give a more precise mass. The compression balance is more useful if you need to measure the mass of objects over 1 kg.
-
