Sectieoverzicht
-
-
When the wind blows across the surface of the water strongly enough it creates waves. This occurs most often and most powerfully on the ocean because of the lack of land to resist the power of the wind.
Wave energy, also known as ocean energy or sea wave energy, is energy harnessed from the ocean or sea waves. The rigorous vertical motion of surface ocean waves contains a lot of kinetic energy that is captured by wave energy technologies to do useful tasks, for example, generation of electricity, desalinization of water and pumping of water into reservoirs.
When the wind blows across the sea surface, it transfers the energy to the waves. They are powerful sources of energy. The energy output is measured by wave speed, wave height, wavelength, and water density.
The stronger the waves, the more capable it is to produce power. It is not easy to harness power from wave generator plants and this is the reason that they are very few wave generator plants around the world.
Wave power is produced by the up and down motion of floating devices placed on the surface of the ocean. In other words, wind produces waves, and then waves produce energy. As the waves travel across the ocean, high-tech devices capture the natural movements of ocean currents and the flow of swells to generate power.
Terminator Devices
These devices are typically situated perpendicular to the direction of the waves in order to utilize the vertical movement of the surface of the water. In a oscillating water column device, waves push water through an opening below the surface of the device. As the water level within the device rise, the air inside the chamber is compressed and forced out of a turbine to generate electrical power. Oscillating water column devices are most often found on shorelines, but floating systems have been produced as well.
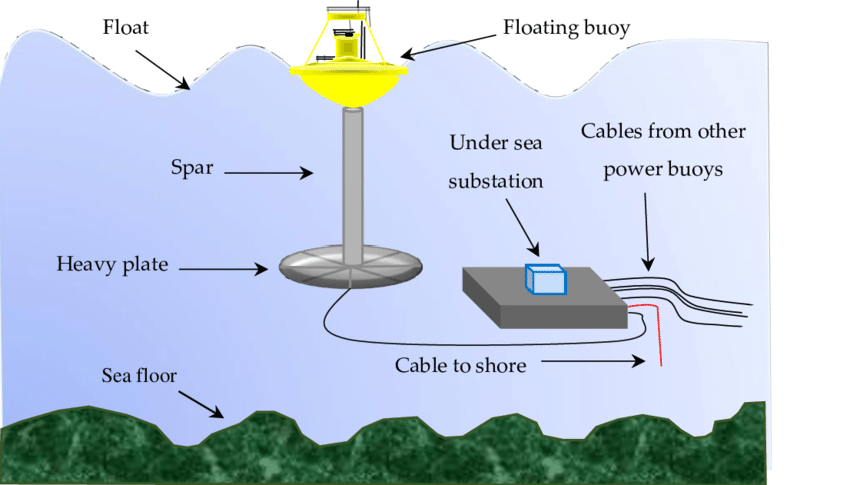
The generator produces electricity, which is transported to electrical grids and later supplied to demand centers and distribution lines that connect individual homes and industries. The advantage of this wave energy converter is that even considerably low wave motions can produce sufficient airflow to maintain the movement of the turbine to generate energy.
Attenuators
Attenuators are long, segmented devices that lie parallel to the direction of the waves. As a wave passes by, different segments are raised and lowered. The motion between segments at differing heights is used to drive hydraulic pumps or some type of converter which can then generate electricity.

Point Absorbers
These devices use the vertical movement of a floating component to either compress a fluid through a turbine, causing rotational motion that can be used for generation of electricity. They are typically more compact than other devices and require some component to be stationary (mounted to the seafloor) while a complimentary component moves due to the waves.

Overtopping Devices
These devices have a reservoir that is filled by incoming waves. As the waves pile up, the water level in the reservoir increases, increasing its potential energy. Much in the same way that a dam on a river does, the water in the reservoir is released through a turbine, and as it flows down into the surrounding water it generates electricity.

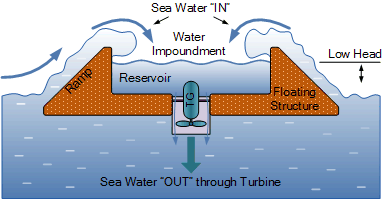
The wave arrival pattern is highly predictable. They arrive day and night and harbor more energy than other renewable sources like wind and solar, but wind speeds die down unexpectedly, which can affect the generation of electricity. The wave magnitude is so unpredictable in the seas. Sometimes it comes vigorously and could cause heavy wear and tear to the wave energy generation turbines. Damage to this equipment can be costly in terms of repair. It would also mean the stalling of electricity supply.
Offshore wave energy projects are sophisticated. The projects include platforms, cables, and turbines. From an ecological standpoint, shallow waters are fertile breeding and resting grounds for most marine life. So, activities from construction and operation of the wave energy plant affect the marine ecosystem. Accidental leaks or spills emanating from hydraulic fluids in the plants could potentially pollute the water resulting in marine life deaths.
-
