Sectieoverzicht
-
-
A capacitor is one of the basic components used in an electrical circuit. A capacitor is a component which is used for storing electrical energy.
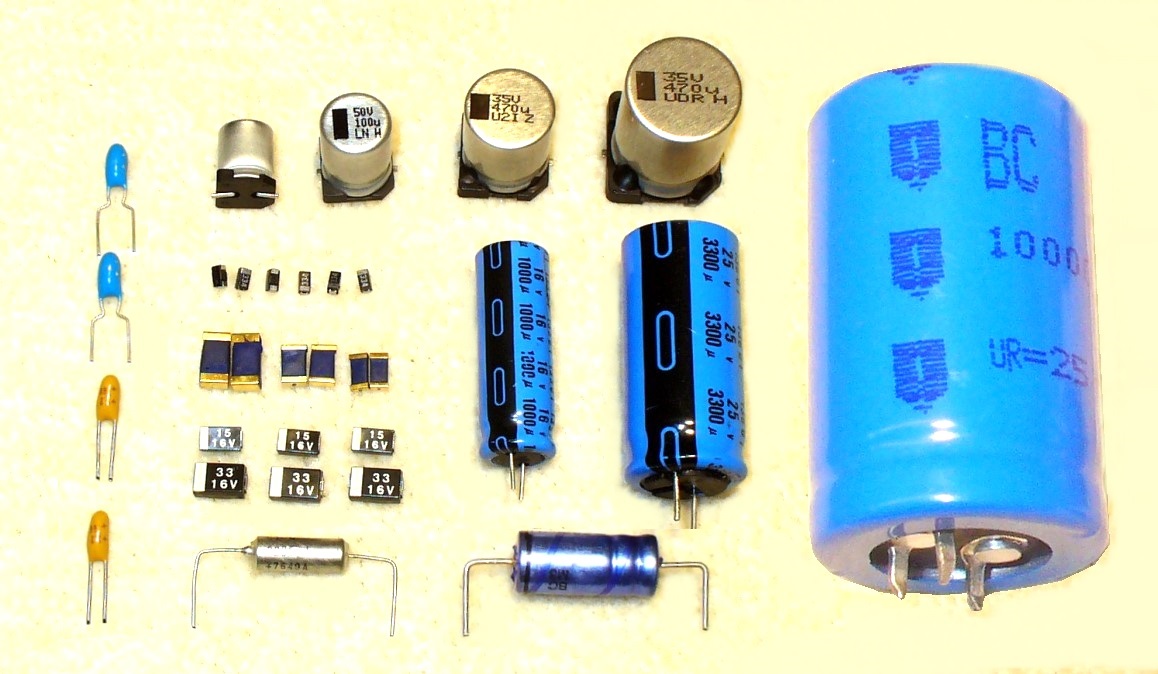
Figure 1: Various different capacitors
A capacitor is made of two electrically conductive plates placed close to each other, but they do not touch each other. The two conductive plates of the capacitor are good conductors of electricity normally made of materials such as aluminum, brass, or copper.
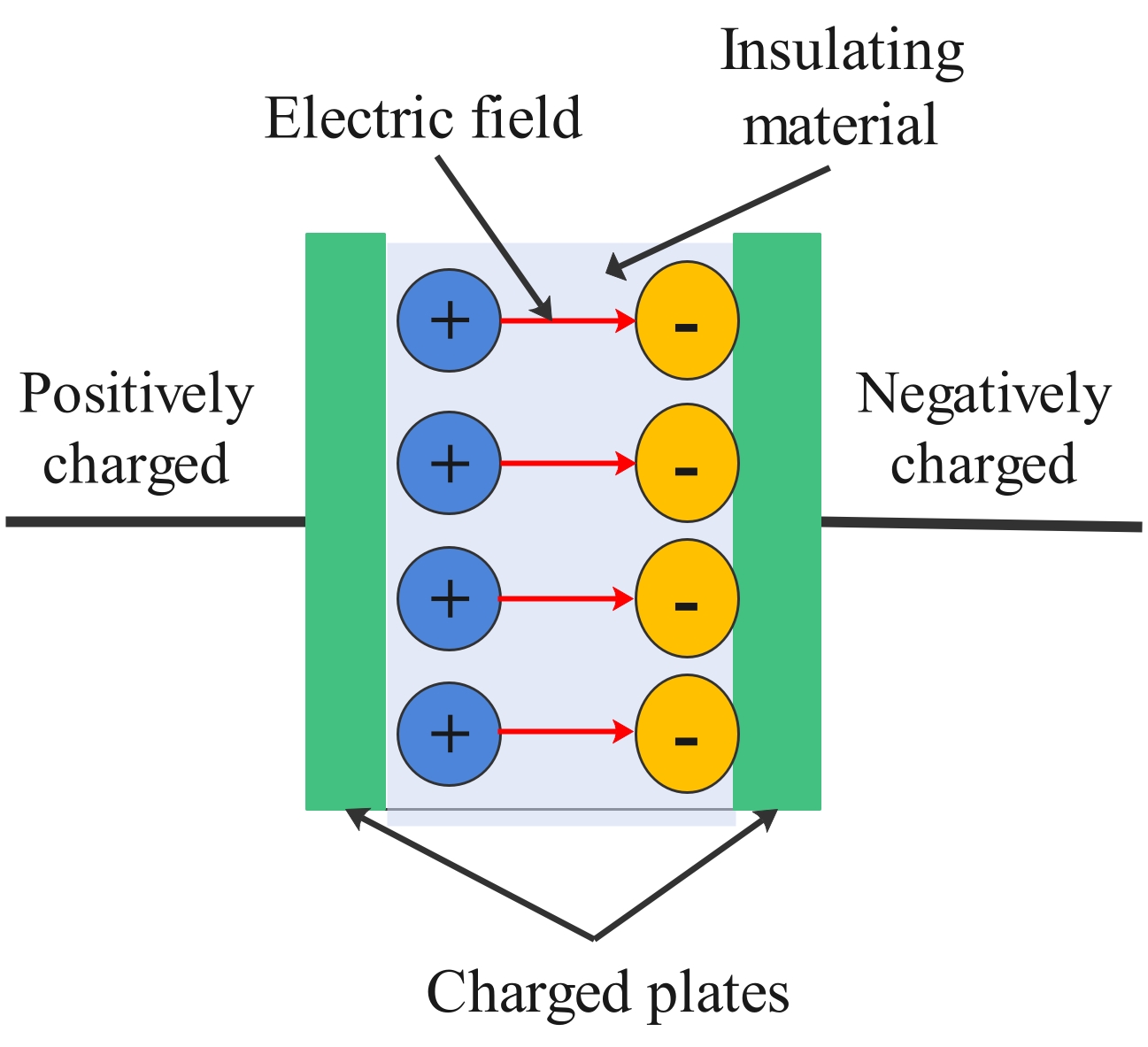
Figure 2: A capacitor diagram. One of the plates is for a positive charge while the other is for a negative charge.
The conductive plates of a capacitor is separated by a small distance. The empty space between these plates is filled with a non-conductive material or electric insulator. The non-conductive material between the two plates may be an air, vacuum, glass, liquid, or solid. They are used because they are poor conductors of electricity.
When the plates are linked to the power, the electric charge builds up on the plates. The positive charge is accumulated on one plate, while the negative charge is accumulated on the other and the electric charges flow easily from one plate to another plate. If the power source connected to the capacitor is removed, the capacitor remains charged.
Capacitors are used widely in electric circuits, and a camera flash is one application that make use of capacitors in real life. A camera requires an enormous amount of energy in a short time to produce a flash that is bright enough to light up the subject of the photograph. Just using the camera's battery is not enough to generate such a huge amount of power, which is why several capacitors are used in the camera to store the energy needed.
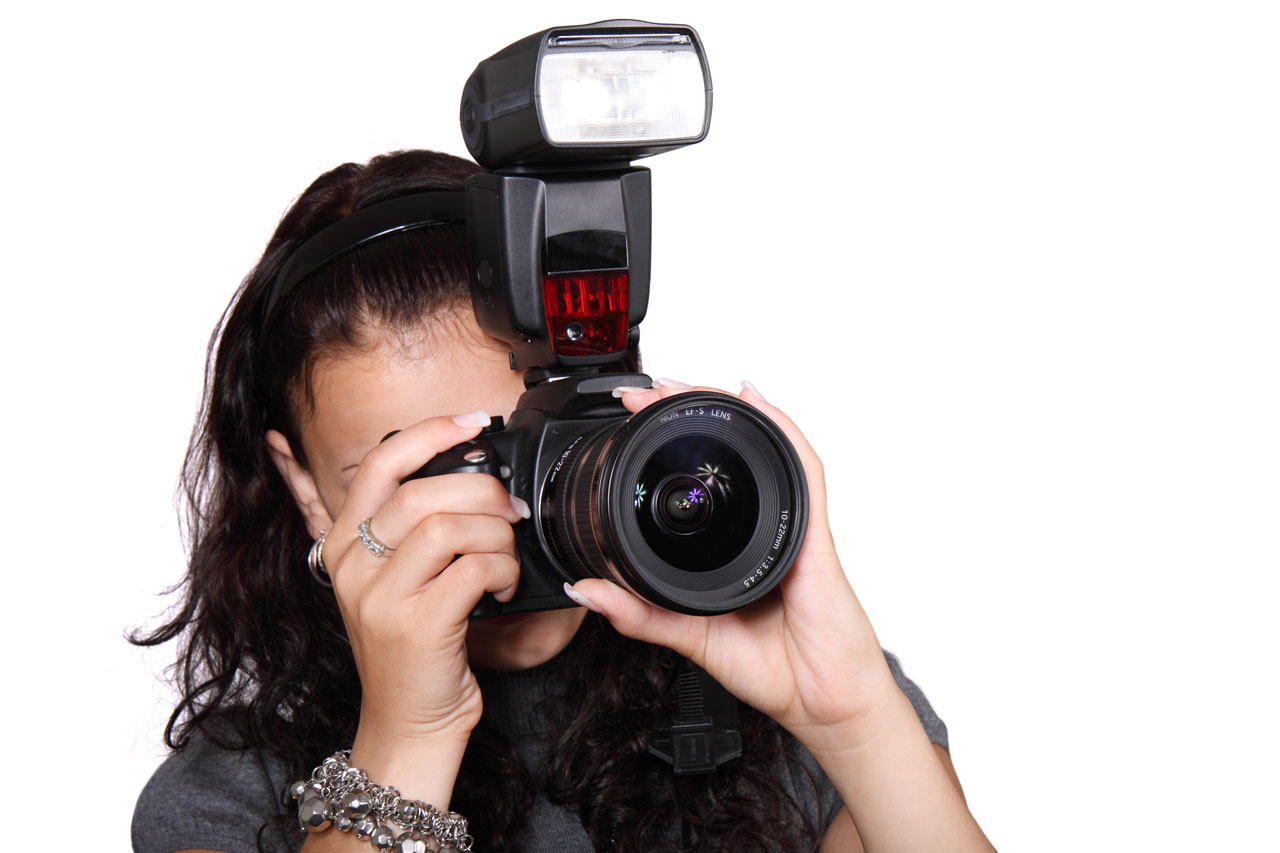

When the flash is used the capacitors discharge quickly and the charged particles flow towards the light bulb circuit at a rapid rate, and so generate a flashlight which illuminates the object for a few seconds.
-
