Sectieoverzicht
-
-
Conductors
Some materials let electricity pass through them easily. These materials are known as electrical conductors.
Many metals, such as copper, iron, and steel, are good electrical conductors. That is why the parts of electrical objects that need to let electricity pass through are always made of metal.
Metal is used in plugs to allow electricity to transfer from the wall socket, through the plug, and into a device such as a radio or TV.
In a light bulb, the metal filament conducts electricity and causes the light bulb to light up.
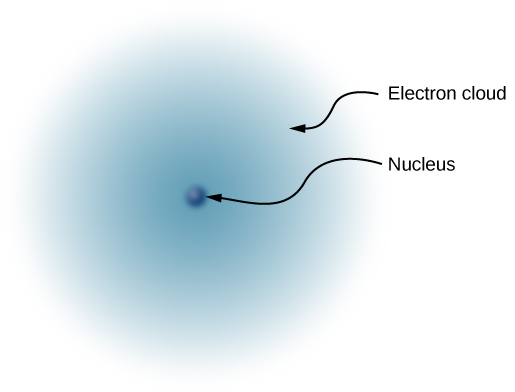
Figure 1: An electron cloud showing that electrons do not have a fixed position in the space around the nucleus of an atom.
In a large mass of copper atoms (such as a copper wire or a sheet of copper), there are vast numbers of outermost electrons (one per atom) which wander from atom to atom and are the electrons that do the moving when electricity flows. These wandering, or “free,” electrons are called conduction electrons, and copper is therefore an excellent conductor of electric charge.
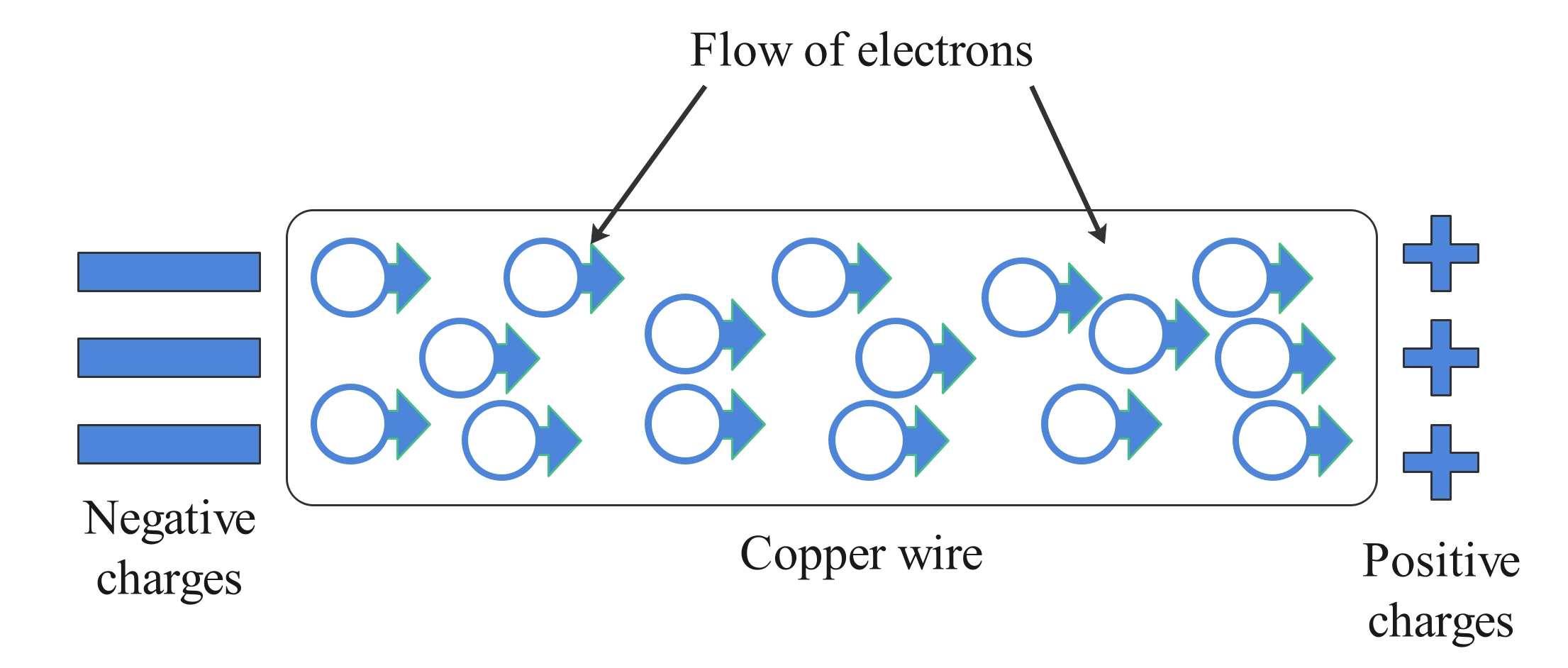
Figure 2: Electricity is the flow or movement of free electrons through a conducting material, such as a metal wire, toward an area of positive electric charges.
All conducting elements have a similar arrangement of their electrons, with one or two conduction electrons. This includes most metals.
Insulators
Some materials do not allow electricity to pass through them. These materials are known as electrical insulators.
Plastic, wood, glass and rubber are good electrical insulators. That is why they are used to cover materials that carry electricity.
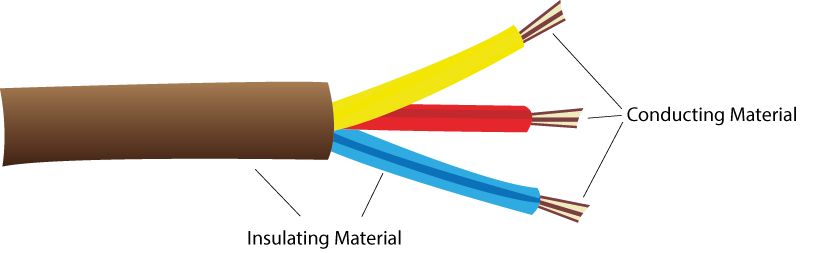
Figure 3: The plastic covering that surround the wires is an electrical insulator. It stops you from getting an electrical shock.
Insulators are made from materials that lack conduction electrons. Even if excess charge is added to an insulating material, it cannot move, remaining indefinitely in place.
Charge cannot flow along or through an insulator, so its electric forces remain for long periods of time. Charge will dissipate from an insulator, given enough time.
Graphite is the only nonmetal which is a conductor of electricity.
Other carriers of current
Electrons are not the only carriers of electric current. Many important electric currents, including the currents along the nerve fibers in your brain and body at work right now, are propagated by ions, atoms or molecules that contain more or fewer electrons than the number of protons, so they have a non-zero charge.
Activity 1
1. Click on the link below:
2. Using the components on the left-hand side, construct a circuit with a bulb, battery, and wires. When connecting the bulb, connect the wire to the red circle on the side of the bulb.
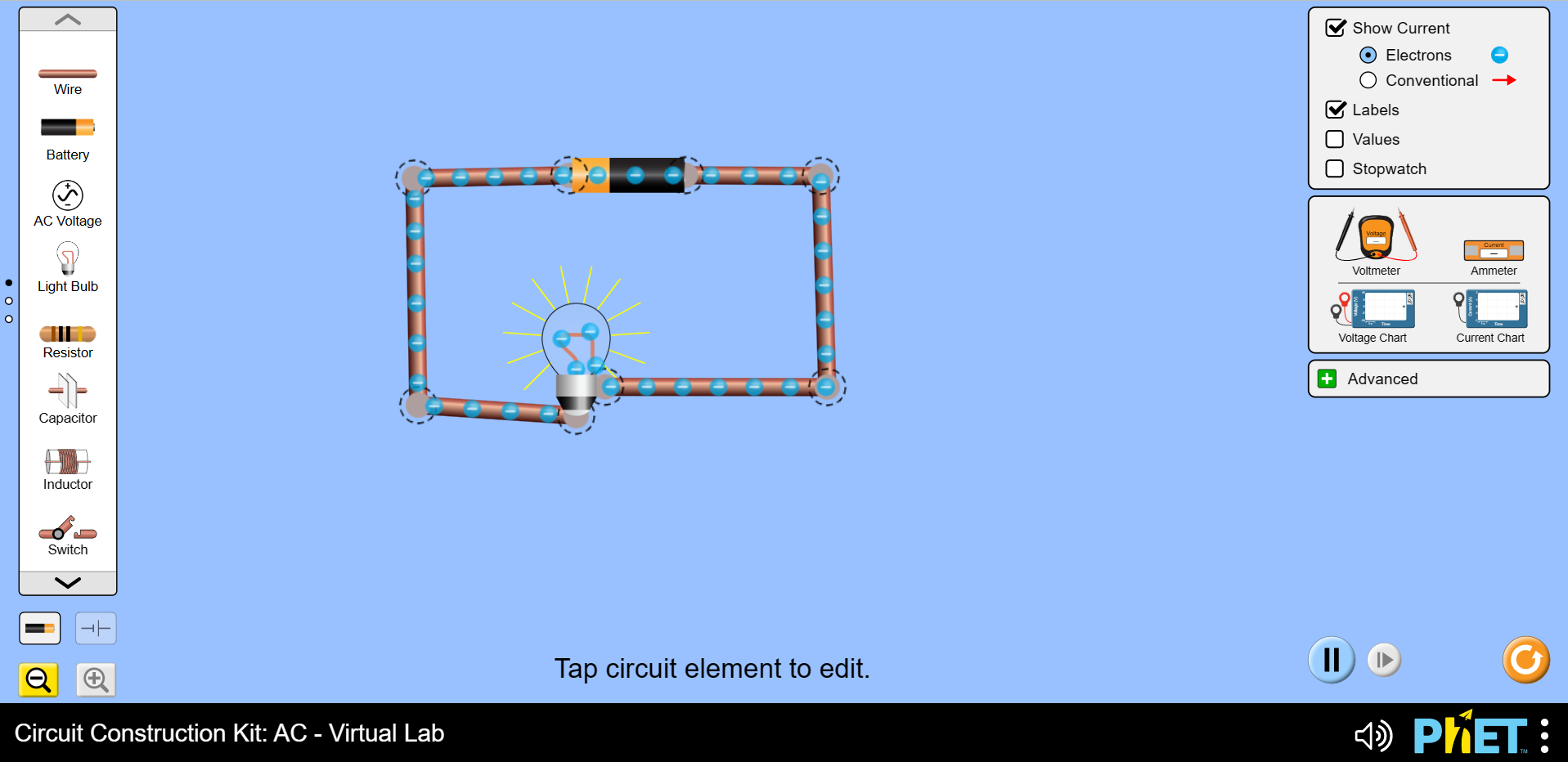
Can you see the flow of electrons in the circuit.
3. Remove the wire connecting the bulb to the rest of the circuit. Scroll through the list of components until you find the coin, hand, eraser, pencil, and dollar bill. Place each component in turn into the circuit. Make a note of which components allow the current to flow and which do not.
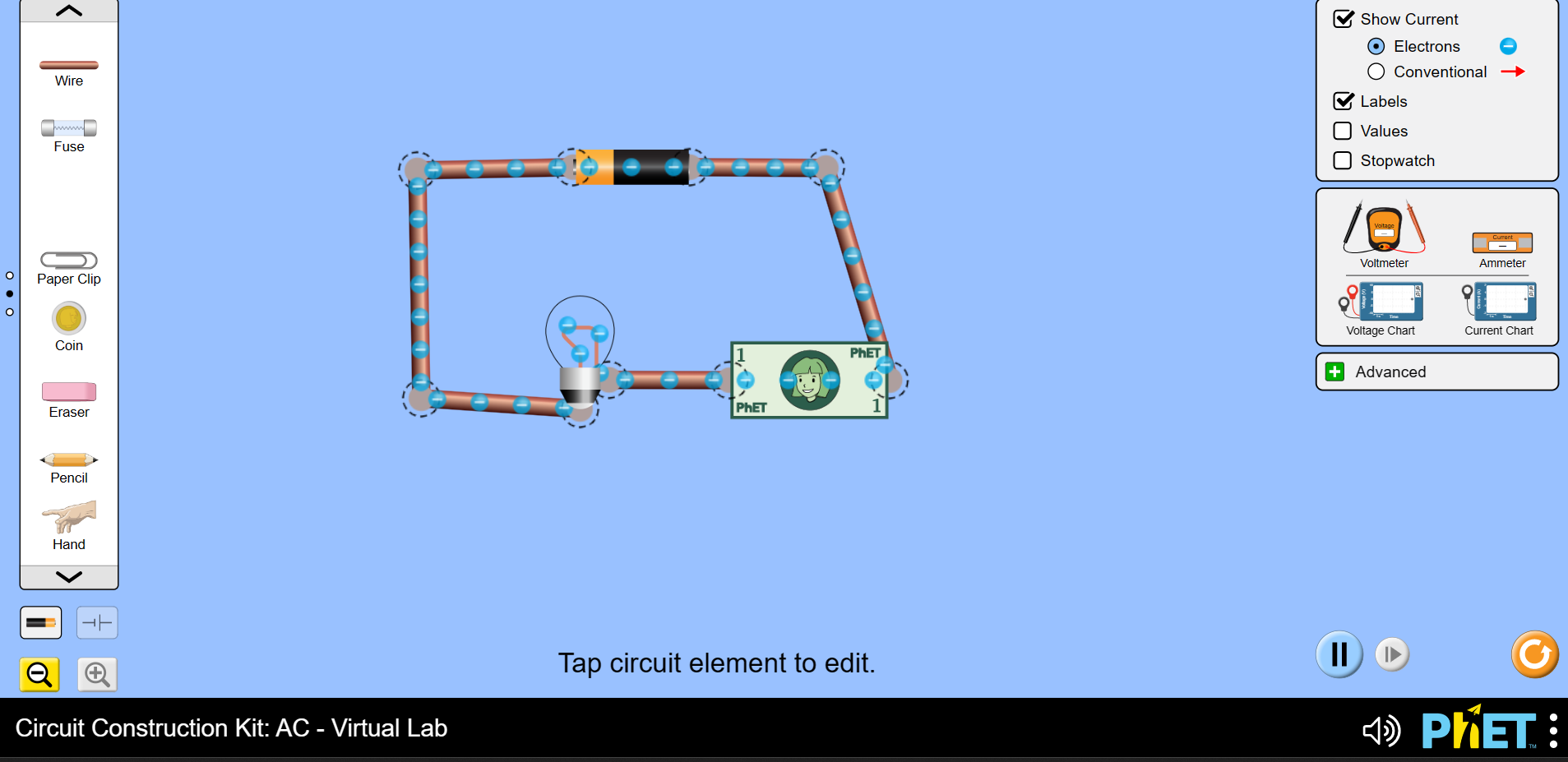
Conclusion:
Insulators: the paper money dollar bill, the eraser, the dog, and the hand, do not conduct electricity.
The paper clip, coin, and the pencil will conduct electricity because they are conductors of electricity. The paper clip and coin are made of metal. The pencil is made from graphite, which is the only nonmetal which conducts electricity.
-
